What's new in MetaTrader 5
The history of updates of the desktop, mobile and web platforms
The latest versions of the MetaTrader 5 mobile app for iOS introduce a range of new features designed to help traders stay abreast of financial markets wherever they are.
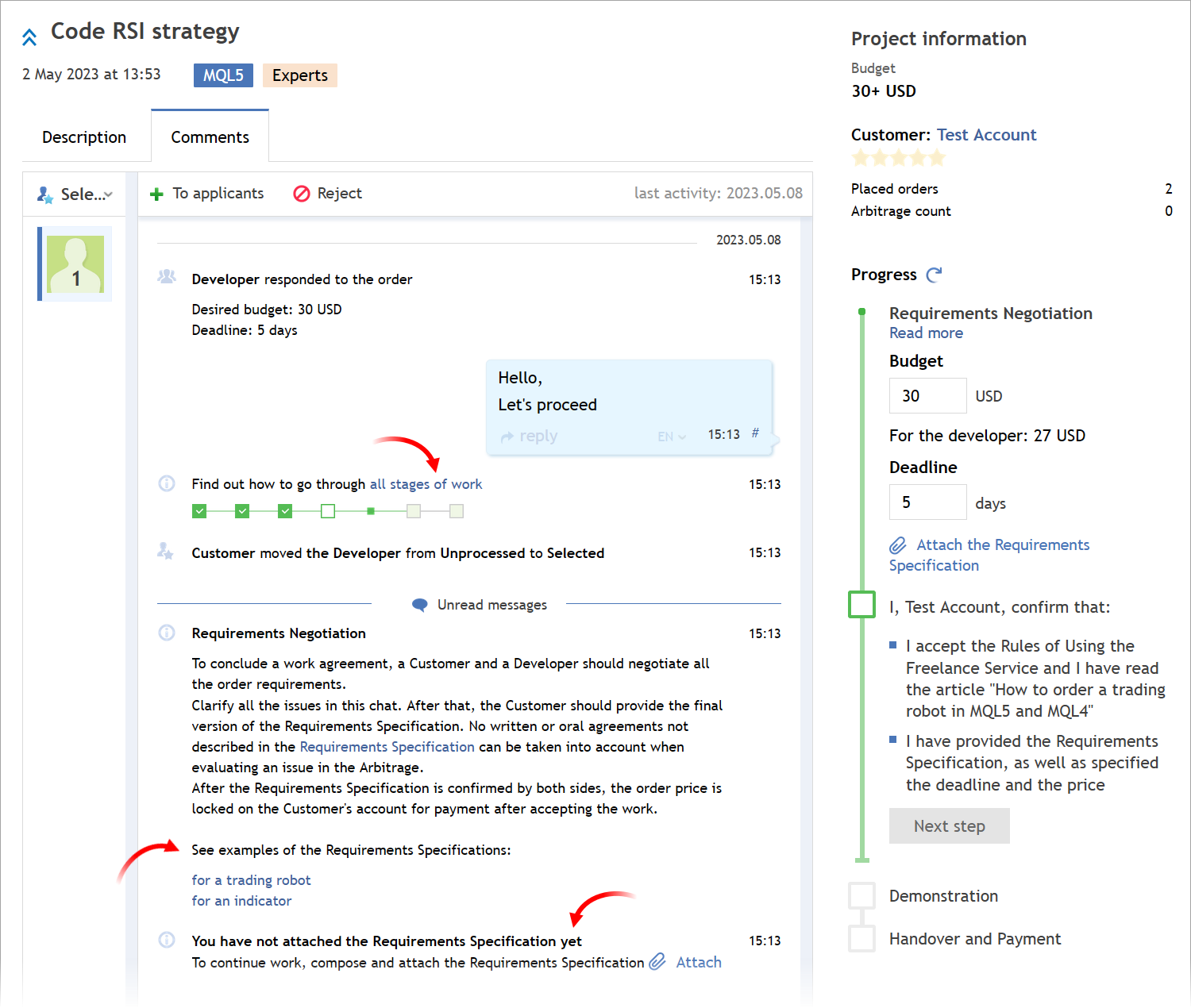
- Added the report
representing trading results in a convenient visual format. It assists
in evaluating trading performance, optimizing portfolios and finding
methods to achieve lower risks along with improved trading stability. To
analyze your strategy, go to the history section and tap the period
selection icon. Next, select the period and tap "Create a trade report".
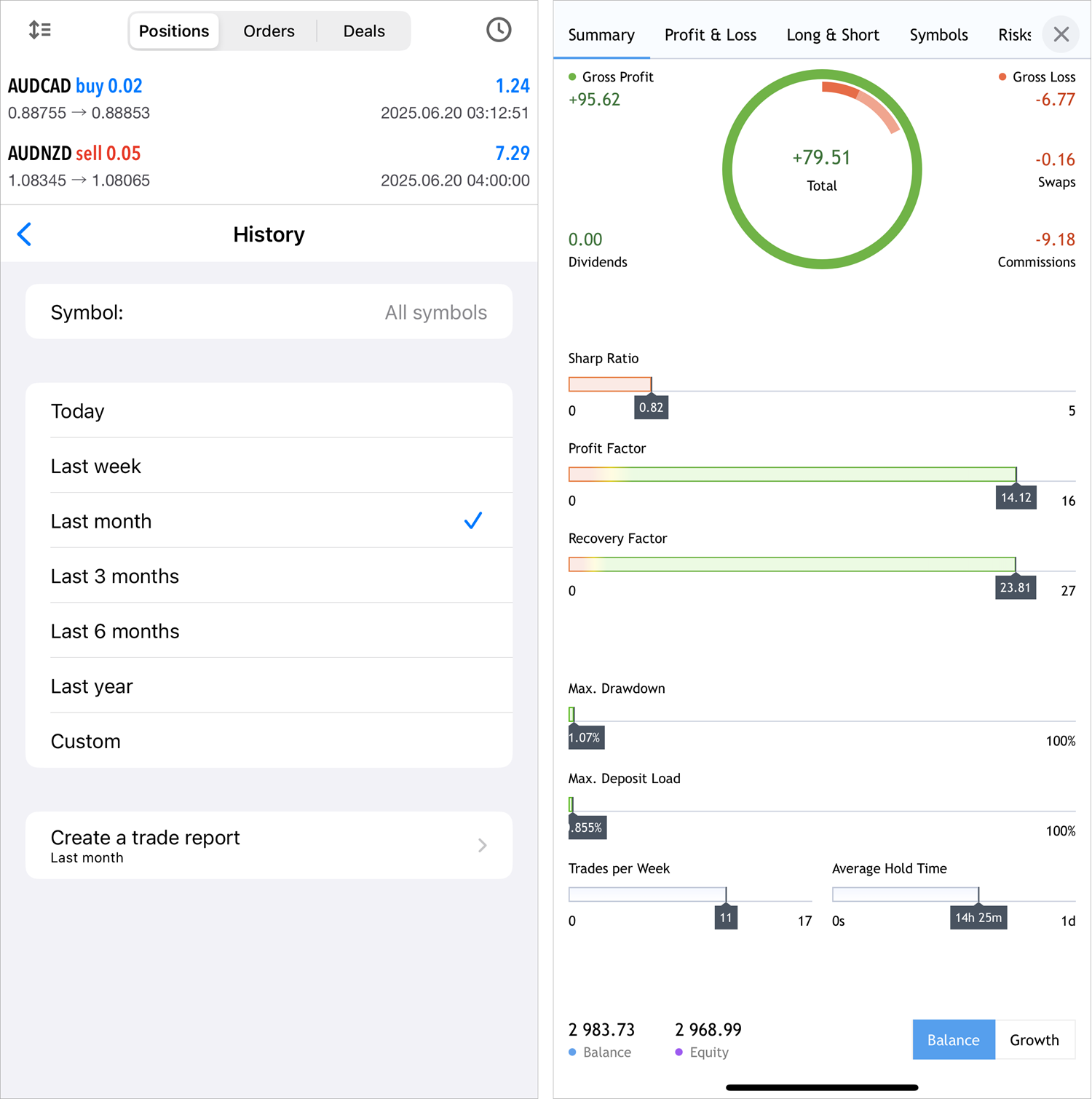
The report is divided into tabs, each providing aggregated information:
- Summary — an overview of trading over time: overall profit and loss metrics, deposit and withdrawal amounts, balance, growth and dividends graphs, and other trading results.
- Profit/Loss — data on profitable and losing trades. The parameter is divided by types of trading (manual, algorithmic and copying trades). The results can be analyzed in terms of trades or money by months and years.
- Long/Short — dynamic ratio of purchases and sales at specified periods of time, as well as Buy and Sell profitability.
- Symbols — analysis of trades by financial instruments. Here you will see which symbols you earn or lose on, how often you trade them, graphs of trades and monetary volumes for them.
- Risks — key risk characteristics of your strategy: drawdown and deposit load graphs, and the ratio of profitable and losing trades.
- Added ZigZag and Market Profile indicators, as well as a new chart type — Heikin Ashi. These tools will enhance market analysis and trend identification.
To add new indicators, open the chart menu, tap Main window and select them from the list. ZigZag is found under trend indicators, while Market Profile belongs to volume indicators.
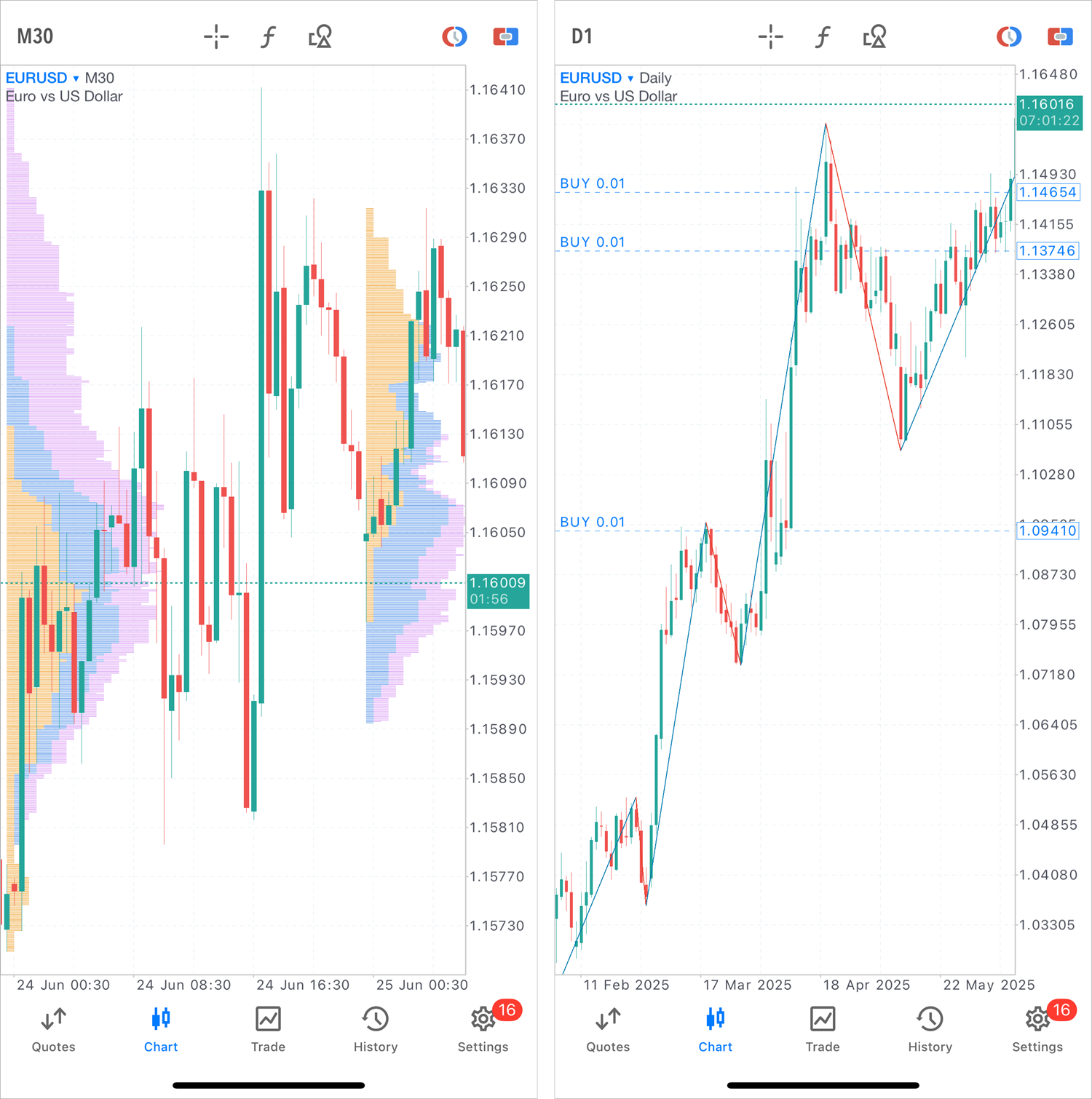
To view the Heikin Ashi chart, tap on the chart and access the settings.
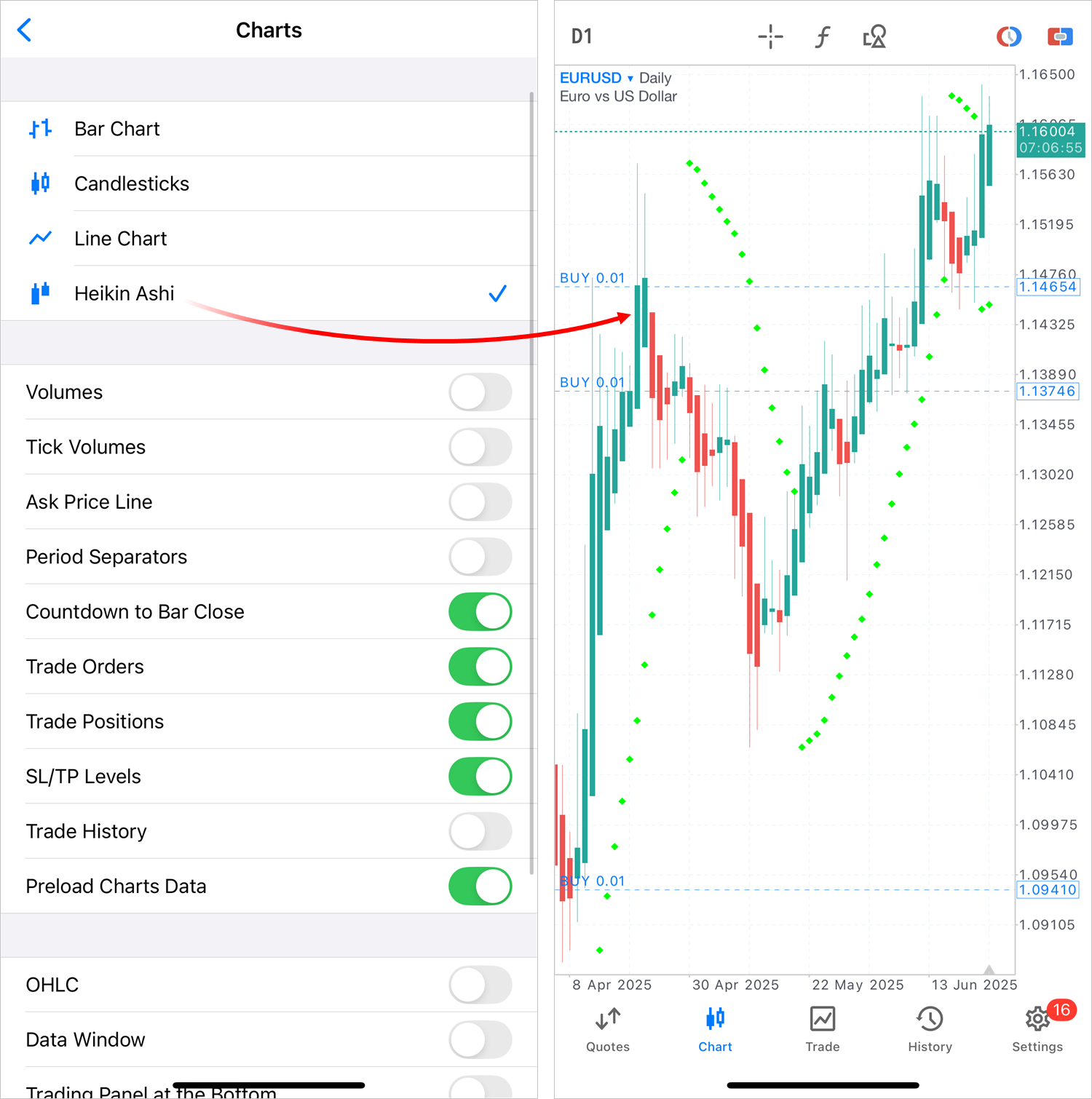
- Added deal info to the Data Window.
When hovering the crosshair over a bar containing deals, the Data
Window will show general info about the transaction: direction, ticket,
volume, price and financial result, along with prices and indicator
values.
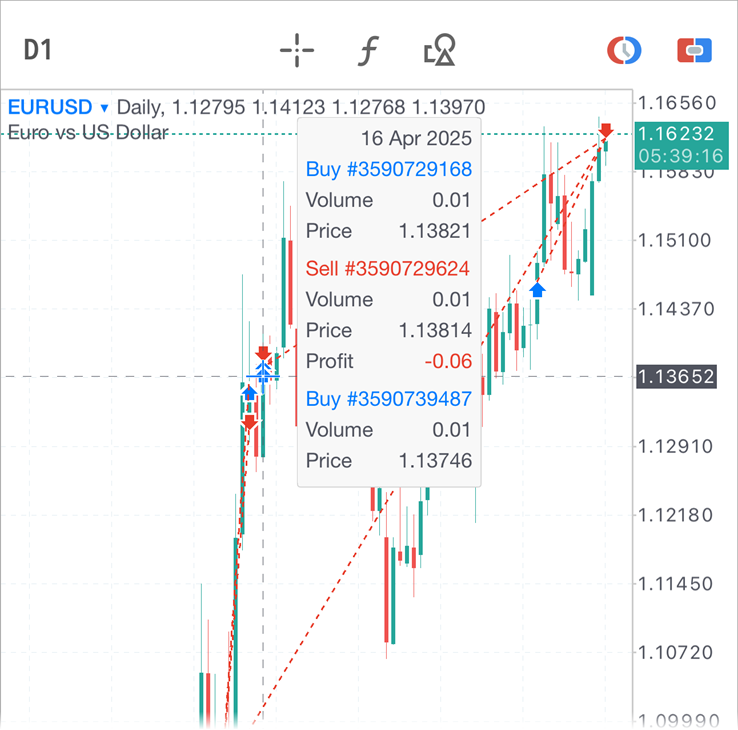
- Added the quick mode for displaying the Data Window on a chart. Tap and hold the main chart for over a second to enable the crosshair mode together with the Data Window. As soon as you release your finger, the chart returns to normal mode. This allows for quick view of the exact values of bars, indicators and deals without switching to crosshair mode via the top panel.
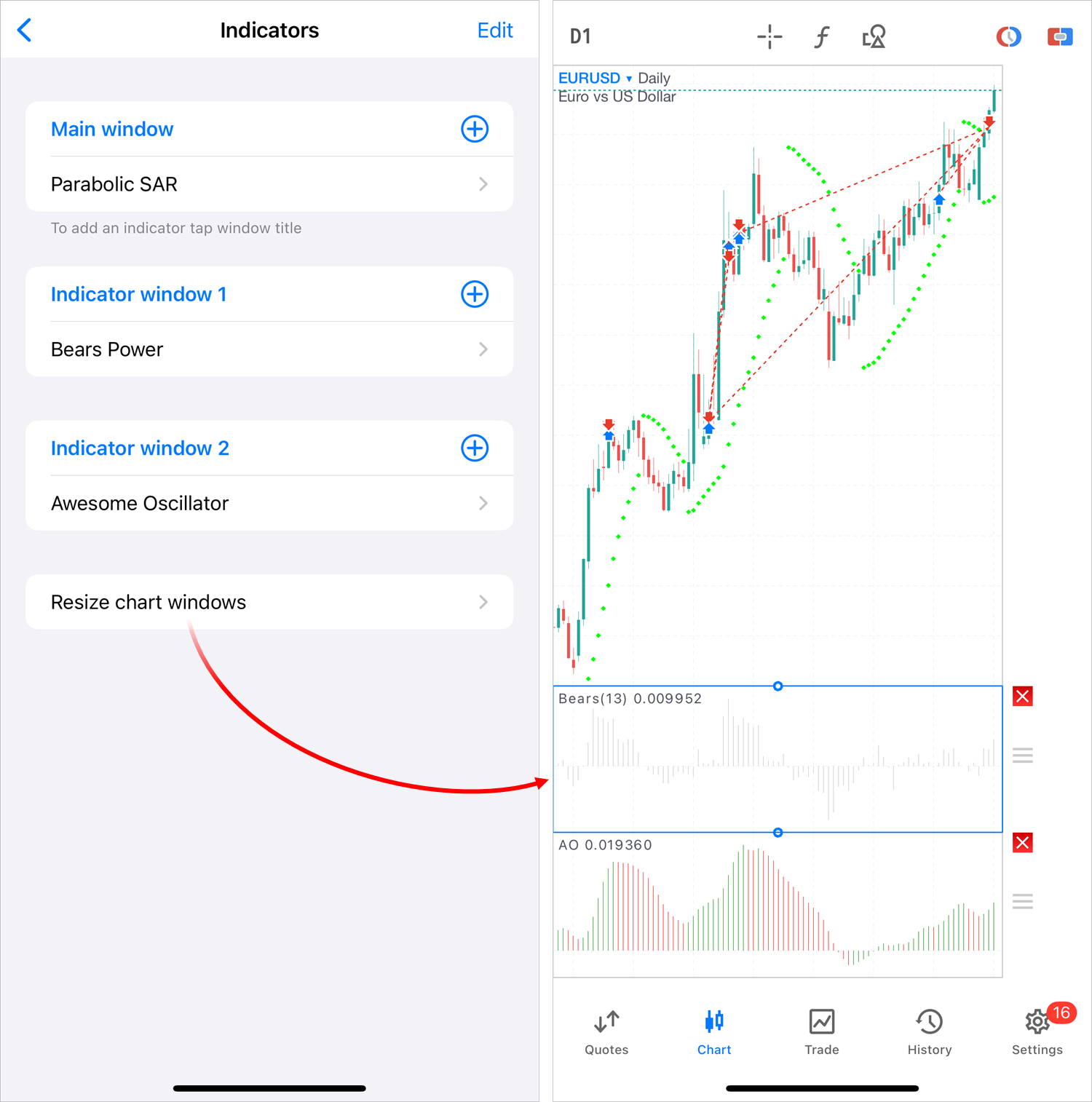
- Added a separate command for resizing and reordering additional
indicator windows. The same action can be performed by long pressing the
indicator subwindow on the chart. Also, improved the subwindow editing
mode itself with additional icons for clarity.
- Optimized trading history display on the chart. The application can now display thousands of deals without significant performance degradation.
Install the latest app version and unlock extended trading capabilities:
 |
|
Terminal
- Fixed graphical interface display issues when running on Linux and macOS.
- Improved the platform update mechanism. The MQL5 Standard Library will no longer be entirely overwritten during updates – only the files that have actually changed will be replaced.
- Added automatic reset of full-screen view mode on application restart. The full interface will now be displayed at each launch.
MQL5
- Enabled passing of arrays with signed/unsigned typecasting in the following functions:
- ArraySwap
- WebRequest
- CryptEncode
- CryptDecode
- StringToCharArray
- CharArrayToString
- StringToShortArray
- ShortArrayToString
- StructToCharArray
- CharArrayToStruct
- Fixed retrieval of key states for MQL programs on the active chart using the TerminalInfoInteger function.
- Fixed ArrayInitialize function operation for enum arrays.
MetaEditor
- Updated available models for AI Assistant. All GPT-4.1 and 04-mini models are now supported.
- Enabled strict file status verification in MQL5 Storage. File hashes are now checked to prevent false indications. Previously, files without actual local changes compared to the repository version could be incorrectly marked with a red icon.
- Updated translations of the user interface.
MetaQuotes Language Editor
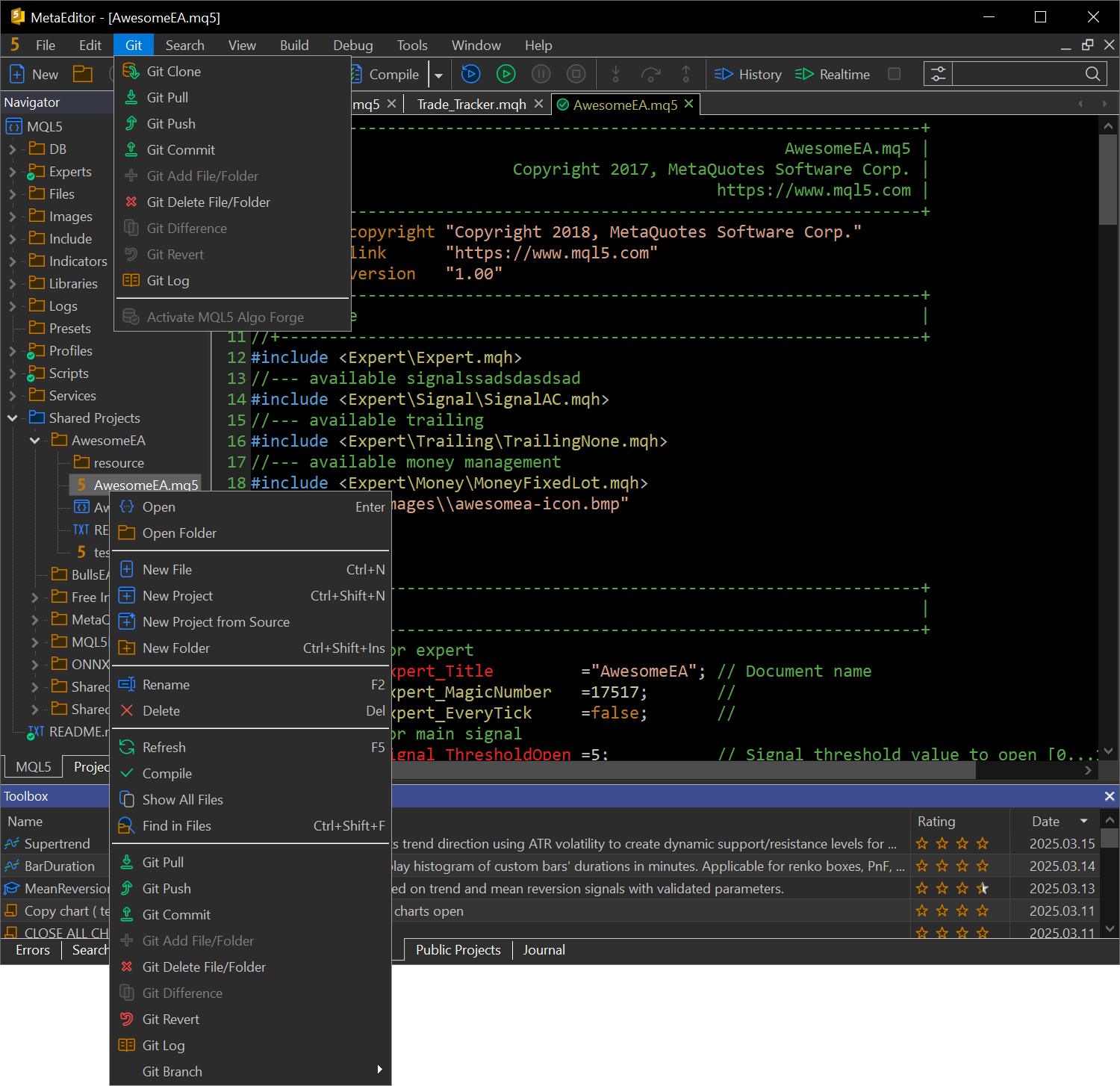
- We have completely revised MQL5 Storage, replacing Subversion with Git as the version control system. Git is the global standard for developers, offering enhanced reliability and flexibility in code management.
- Flexible branching and merging – create separate branches for new features or experiments and easily merge them into the main project version.
- Faster repository operations – unlike Subversion, Git stores all data locally, making commits, version switching, and change comparisons significantly faster.
- Offline work capability – no need for a constant server connection: commit changes locally and push them to an online repository whenever convenient.
- Advanced change tracking – easily review version history, track modifications with timestamps and authors, and revert to previous versions without complications.
- Superior merge functionality – advanced comparison and merge tools help minimize conflicts and streamline collaborative development.
A new level of collaborative development
With the transition to Git, we are introducing MQL5 Algo Forge, a new online portal for project management. More than just a project list, it is a full-fledged social network for developers – essentially, GitHub for algorithmic traders. Follow interesting developers, create teams, and collaborate on projects effortlessly.
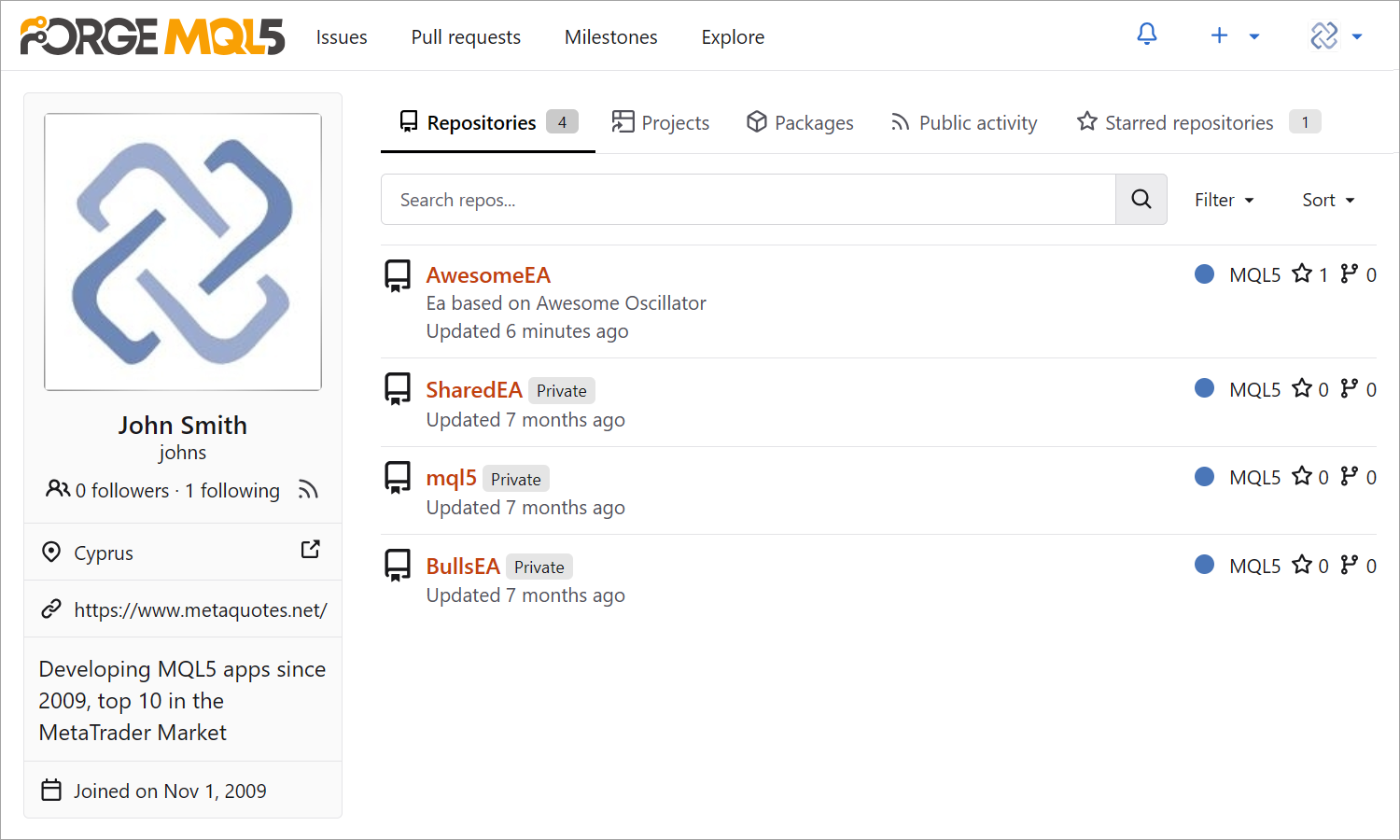
View project details: structure, files, commits, branches, and more. Track individual contributions, create documentation, and share projects online.
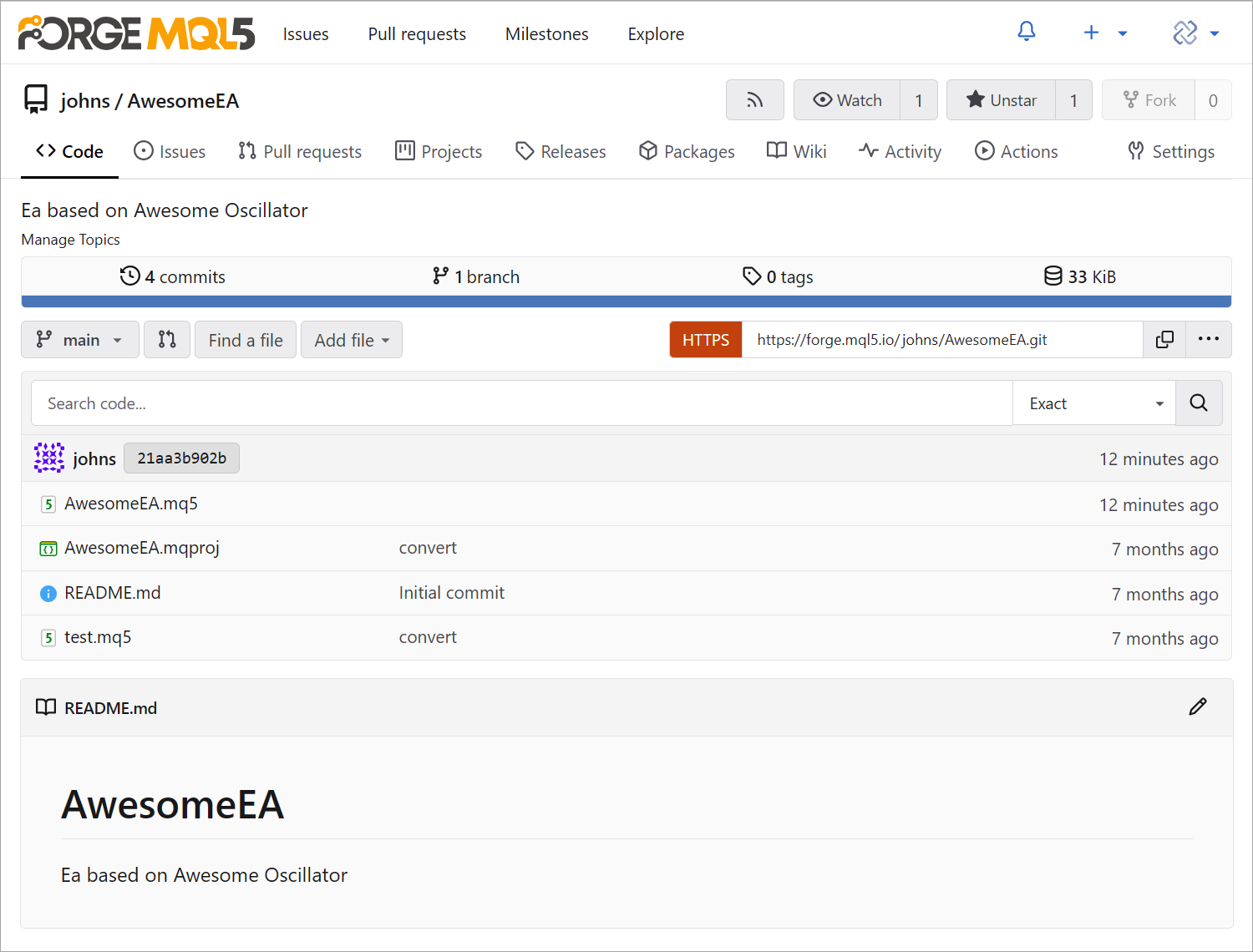
Monitor all code changes: detect new, modified, and deleted lines. If issues arise, assign tasks to developers directly within the project.
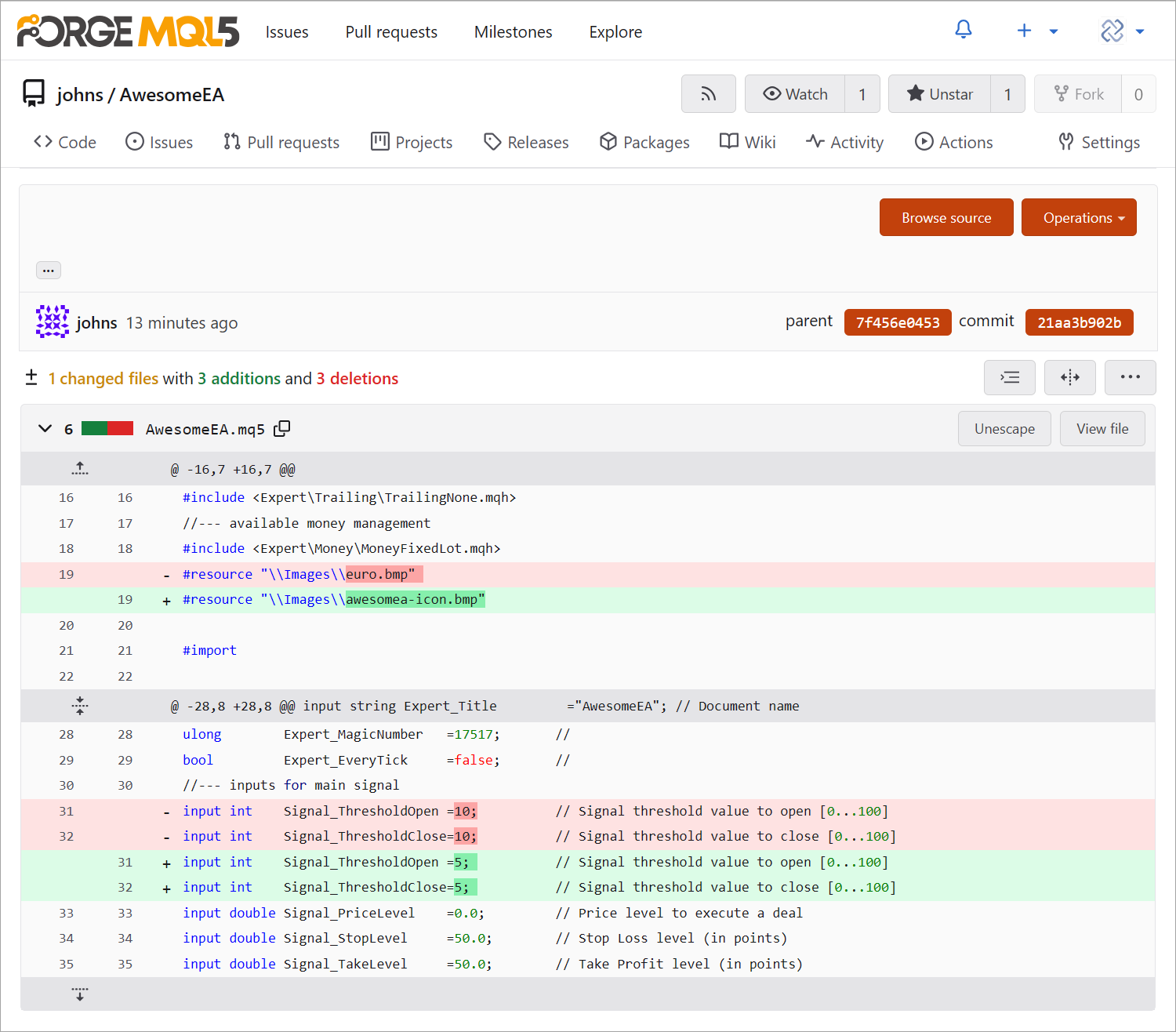
To enhance Git usability, we have redesigned the Navigator and the active code editing window. We have also introduced a dedicated Git menu on the MetaEditor toolbar:
Comprehensive Git documentation will be available soon.
Terminal
- Added support for a dark color scheme for all components, including the trading terminal, MetaEditor, and the visual tester. The dark theme offers a more comfortable development experience at night. Use the View menu to switch:
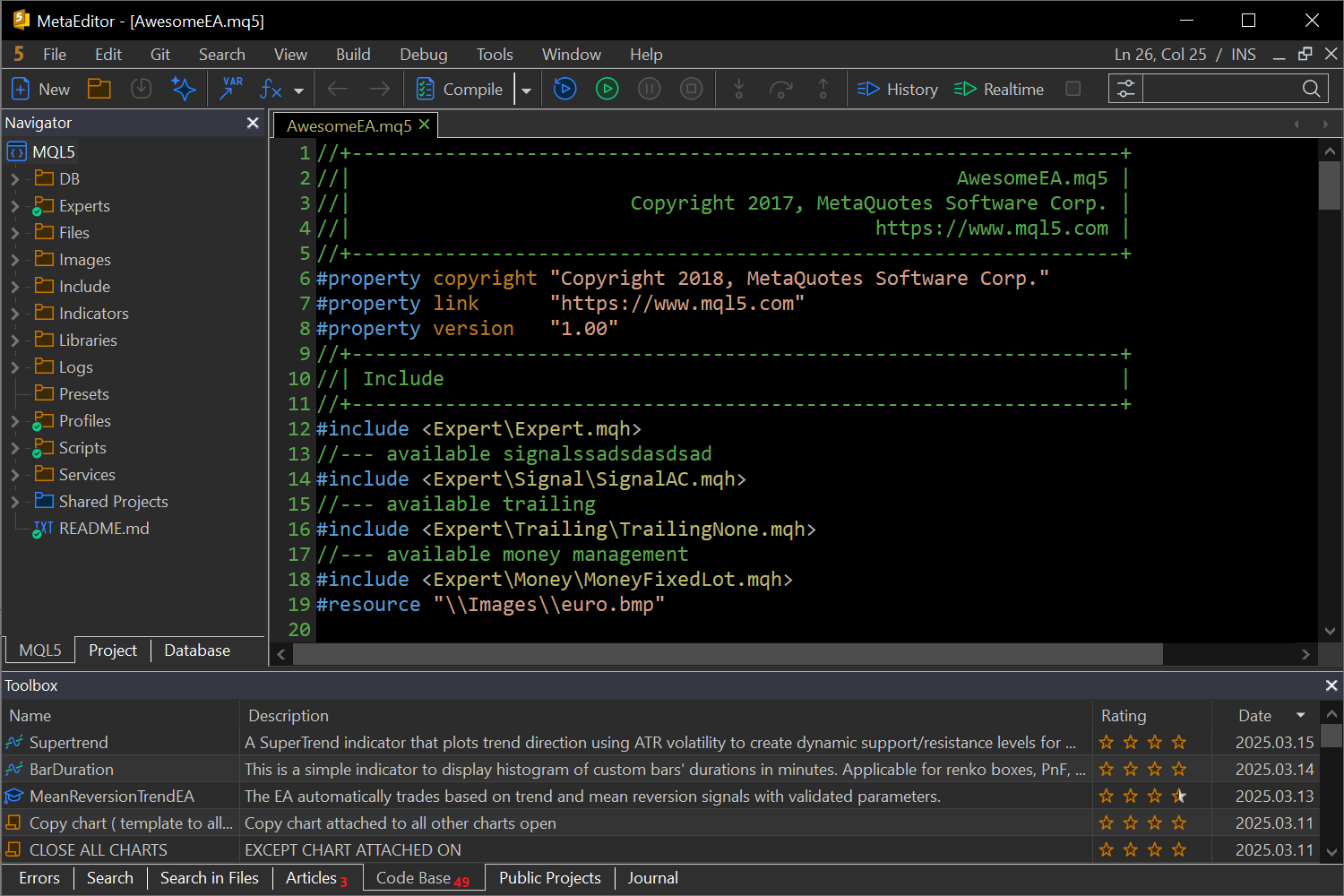
While adapting the interface to support different themes, we have introduced numerous improvements to the display of dialogs, menus, panels, and buttons for a more comfortable user experience. In MetaEditor, cursor position information and the text input mode indicator (INS/OVR) are now displayed in the upper-right corner. The bottom status bar has been removed to save the workspace.
- Added 12-month VPS rental option. By purchasing long-term hosting upfront, you save one-third of the total cost.
- Optimized memory usage. The terminal now consumes fewer system resources, resulting in improved performance.
- Optimized display of account trading history. The platform can now display millions of records correctly.
- Added "Reset to default" command to the Window menu. It resets all interface elements, including charts, Navigator, Strategy Tester, and others, to their original positions.
- Fixed error causing position modification dialog to freeze under certain conditions.
- Fixed value calculation for open positions with negative prices.
- Fixed margin rate calculations in trading symbol specifications with negative prices.
- Fixed calculation of current MFE and MAE values and display of their graphs in trading reports.
- Fixed scaling of oscillators in chart subwindows. The vertical scale for oscillators is now displayed correctly.
- Fixed visibility of order books and option boards when switching the full-screen mode.
- Added position ticket display in account trading history. Use the context menu to enable the relevant column.
- Fixed liquidation value calculation on the Exposure tab for futures and options.
- Fixed issue with copying newly created account data to the clipboard. During the final step of demo or preliminary account registration, the user is provided with account details: login, passwords, etc. These can be copied to the clipboard to save in a separate file. The corresponding command now functions correctly on macOS.
- Fixed display of the VPS log section. The page could display an error under certain conditions.
- Fixed HiDPI monitor support on Linux.
- Updated translations of the user interface.
MQL5
- Added matrix multiplication operator @. It follows linear algebra rules and allows the multiplication of matrices and vectors, as well as scalar (dot) products of vectors.
Matrix multiplication (matrix × matrix)
matrix A(2, 3); matrix B(3, 2); matrix C = A @ B; // Result: Matrix C of size [2,2]
Matrix multiplication (matrix × vector)
matrix M(2, 3); vector V(3); vector R = M @ V; // Result: Vector R of 2 elements
Matrix multiplication (vector x matrix)
matrix M(2, 3); vector V(1, 2); vector R = V @ M; // Result: Vector R of 3 elements
Scalar multiplication (vector × vector)
vector V1(1, 3), V2(1, 3); double r = V1 @ V2; // Result: Scalar
- Added 'ddof' parameter in methods Std, Var, and Cov. This parameter defines the number of degrees of freedom subtracted from the denominator when calculating the standard deviation. For Std and Var, the default parameter is 0, for Cov it is 1.
How ddof affects calculation:
- By default, ddof=0, meaning the population standard deviation is calculated.
- If ddof=1, the function computes the sample standard deviation, which adjusts for finite sample sizes, commonly used in statistics when analyzing a subset of data.
- Added new OpenBLAS methods:
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- EigenTridiagonalDC – computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a symmetric tridiagonal matrix using the divide-and-conquer algorithm (LAPACK function STEVD).
- EigenTridiagonalQR – computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a symmetric tridiagonal matrix using the QR algorithm (LAPACK function STEV).
- EigenTridiagonalRobust – computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a symmetric tridiagonal matrix using the MRRR (Multiple Relatively Robust Representations) algorithm (LAPACK function STEVR).
- EigenTridiagonalBisect – computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a symmetric tridiagonal matrix using the bisection algorithm (LAPACK function STEVX).
- ReduceToBidiagonal – reduces a general real or complex m-by-n matrix A to upper or lower bidiagonal form B by an orthogonal transformation: Q**T * A * P = B. If m≥n, B is an upper bidiagonal matrix; otherwise, B is lower bidiagonal. (LAPACK function GEBRD).
- ReflectBidiagonalToQP – generates orthogonal matrices Q and P**T (or P**H for complex types) determined by ReduceToBidiagonal method when reducing a real or complex matrix A to bidiagonal form: A = Q * B * P**T. Q and P**T are defined as products of elementary reflectors H(i) or G(i) respectively. (LAPACK functions ORGBR, UNGBR).
- ReduceSymmetricToTridiagonal – reduces a real symmetric or complex Hermitian matrix A to tridiagonal form B by an orthogonal similarity transformation: Q**T * A * Q = B. (LAPACK functions SYTRD, HETRD).
- ReflectTridiagonalToQ – generates orthogonal matrix Q which is defined as the product of n-1 elementary reflectors of order n, as returned by ReduceSymmetricToTridiagonal.
- LinearEquationsSolution – computes the solution to the system of linear equations with a square coefficient matrix A and multiple right-hand sides.
- LinearEquationsSolutionTriangular – computes the solution to the system of linear equations with a square triangular coefficient matrix A and multiple right-hand sides.
- LinearEquationsSolutionSy – computes the solution to the system of linear equations with a symmetric or Hermitian conjugated matrix A and multiple right-hand sides.
- LinearEquationsSolutionComplexSy – computes the solution to the system of linear equations with a complex symmetric matrix A and multiple right-hand sides.
- LinearEquationsSolutionGeTrid – computes the solution to the system of linear equations with a symmetric or Hermitian conjugated positive-definite matrix A and multiple right-hand sides.
- LinearEquationsSolutionSyPD – computes the solution to the system of linear equations with a general (nonsymmetric) tridiagonal coefficient matrix A and multiple right-hand sides.
- LinearEquationsSolutionSyTridPD – computes the solution to the system of linear equations with a symmetric tridiagonal positive-definite coefficient matrix A and multiple right-hand sides.
- FactorizationQR – computes the QR factorization of a general m-by-n matrix: A = Q * R (LAPACK function GEQRF).
- FactorizationQRNonNeg – computes the QR factorization of a general m-by-n matrix: A = Q * R, where R is an upper triangular matrix with nonnegative diagonal entries (LAPACK function GEQRFP).
- FactorizationQRPivot – computes the QR factorization of a general m-by-n matrix with column pivoting: A * P = Q * R (LAPACK function GEQP3).
- FactorizationLQ – computes the LQ factorization of a general m-by-n matrix: A = L * Q (LAPACK function GELQF).
- FactorizationQL – computes the QL factorization of a general m-by-n matrix: A = Q * L (LAPACK function GEQLF).
- FactorizationRQ – computes the RQ factorization of a general m-by-n matrix: A = R * Q (LAPACK function GERQF).
- FactorizationPLU – computes an LU factorization of a general M-by-N matrix A using partial pivoting with row interchanges (LAPACK function GETRF).
- FactorizationPLUGeTrid – computes an LU factorization of a general (non-symmetric) tridiagonal N-by-N matrix A using elimination with partial pivoting and row interchanges (LAPACK function GTTRF).
- FactorizationLDL – computes the factorization of a real symmetric or complex Hermitian matrix A using the Bunch-Kaufman diagonal pivoting method (LAPACK functions SYTRF and HETRF).
- FactorizationLDLSyTridPD – computes the factorization of a symmetric positive-definite or, for complex data, Hermitian positive-definite tridiagonal matrix A (LAPACK function PTTRF).
- FactorizationCholesky – computes the factorization of a real symmetric or complex Hermitian positive-definite matrix A (LAPACK function POTRF).
- FactorizationCholeskySyPS – computes the Cholesky factorization with complete pivoting of a real symmetric (complex Hermitian) positive semidefinite n-by-n matrix (LAPACK function PSTRF).
- Added Random function and method for filling vectors and matrices with random values. Random values are generated uniformly within the specified range.
static vector vector::Random( const ulong size, // vector length const double min=0.0, // min value const double max=1.0 // max value ); static matrix matrix::Random( const ulong rows, // number of rows const ulong cols // number of columns const float min=0.0, // min value const float max=1.0 // max value );
- Added support for additional aliases for integer types. This will simplify code porting from other languages such as C and C++.
These aliases do not introduce new types but provide alternative names for existing types in MQL5. They can be used in all contexts where the base types are applicable.
- int8_t
- uint8_t
- int16_t
- uint16_t
- int32_t
- uint32_t
- int64_t
- uint64_t
- Added new functions for detecting the terminal color scheme:
- A new property TERMINAL_COLORTHEME_NAME has been added to the ENUM_TERMINAL_INFO_STRING enumeration. Use this property with the TerminalInfoString function to query the terminal's color scheme. Possible values: Light and Dark.
- New properties THEME_COLOR_* have been added to the ENUM_TERMINAL_INFO_INTEGER enumeration. Use them with the TerminalInfoInteger function to retrieve the colors of specific UI elements.
To detect a color scheme change, use the OnChartEvent handler. When the theme changes, the CHARTEVENT_CHART_CHANGE event is triggered twice. - Fixed a bug that caused MetaEditor to crash when compiling code containing the Array::Reserve method. The 'Reserve' method does not change the array size, but reserves space for the specified number of elements to prevent memory reallocation when adding new elements.
- Fixed the behavior of the Array::Push method, which adds new elements to the end of an array. The issue occurred in arrays with preallocated buffer space.
- Resolved issues in functions for working with OpenCL.
MetaTester
- Accelerated the optimization of trading strategies.
- Fixed a bug that, in certain cases, led to excessive memory usage by tester agents when executing tasks from the MQL5 Cloud Network.
Web Terminal
- Fixed the password-saving option in the account connection dialog.
- Fixed chart movement buttons. In some cases, using these buttons caused the chart to disappear.
- Corrected validation for the "Middle Name" field in the real account registration form. It is now optional.
- Fixed opening of demo accounts. In certain cases, users were incorrectly redirected to the broker's website.
- Fixed the visibility of buttons for opening demo and real accounts. These buttons are now hidden if the respective function is disabled by the broker.
- Fixed the "Deposit" field behavior in the demo account opening form.
- Fixed the display of the "Trading" field in the contract specification.
- Fixed the symbol search field in the "Market Watch" window. The "X" button now correctly appears for exiting search mode.
- Fixed the display of a tooltip for the email confirmation code field in the account opening form.
The update will be available through the Live Update system.
The latest versions of the MetaTrader 5 mobile app for iOS introduce a range of convenient chart features, along with important stability improvements for a smoother user experience.
- Added text object for creating custom labels on charts. Open the chart objects menu and tap "Add Text". Next, enter your desired text and select a point on the chart to place the label. An object has two points: one for moving and another for adjusting direction.
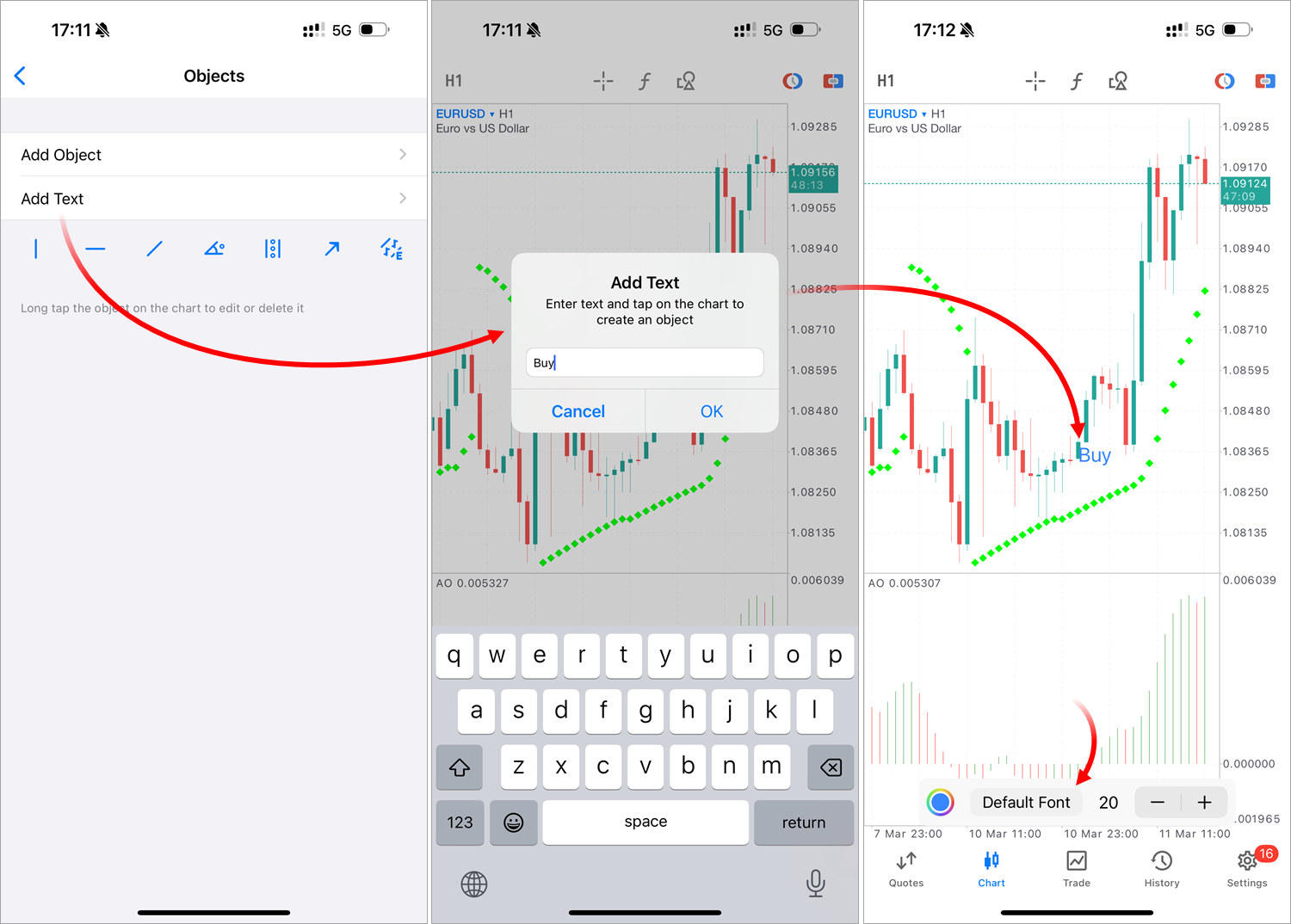
We've also added a small on-chart objects menu, which appears at the bottom of the screen immediately after creating an object. You can now modify key properties without navigating to the full objects menu. - Added countdown timer that displays the remaining time until the current bar closes. It works across all timeframes, from minute to daily charts. This feature will be especially useful for traders whose strategies depend on bar openings and closings.
To enable the timer, go to chart settings. The countdown is displayed on the vertical scale below the current price.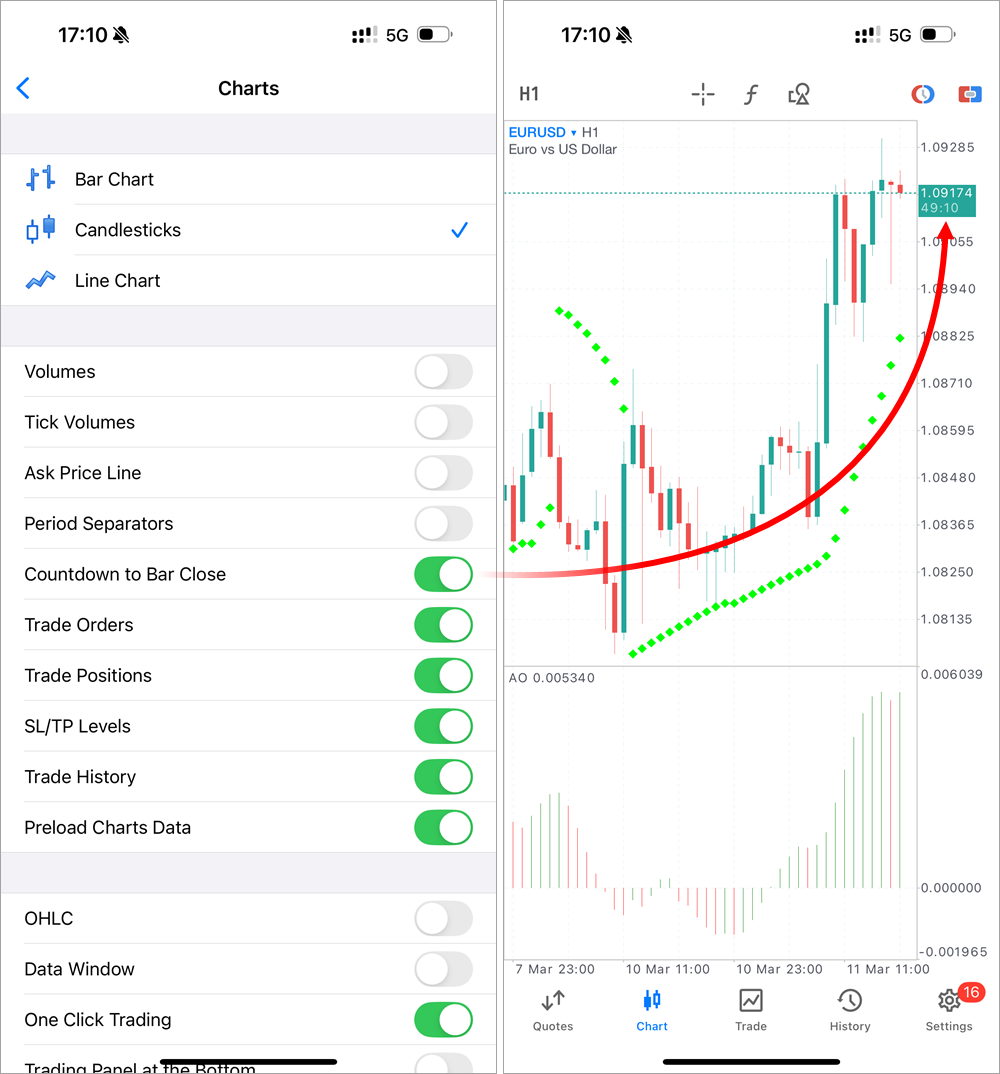
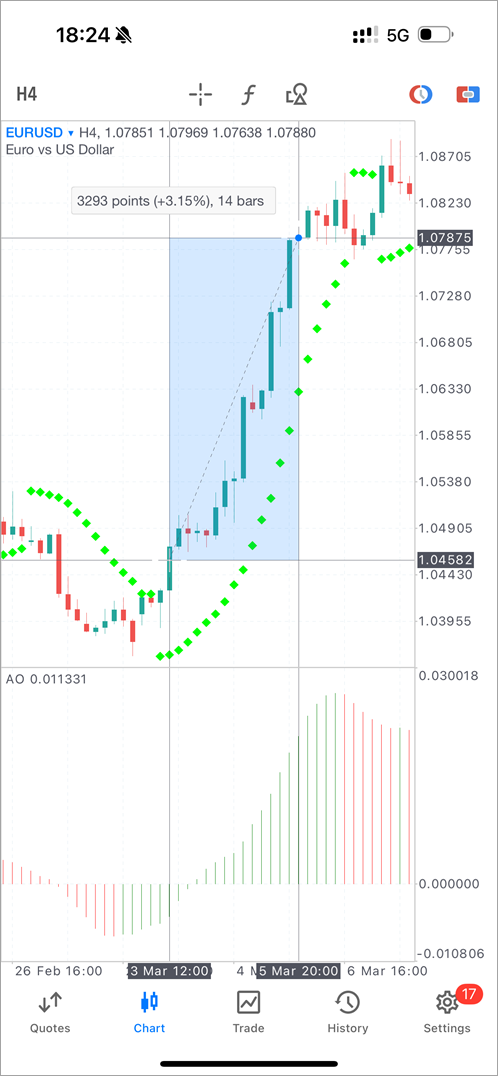
- Enhanced crosshair mode – it can now be used as a ruler. Activate the crosshair and place it at the desired starting point. Then tap the endpoint to measure the distance. The tooltip will display the difference in price, percentage, and number of bars.
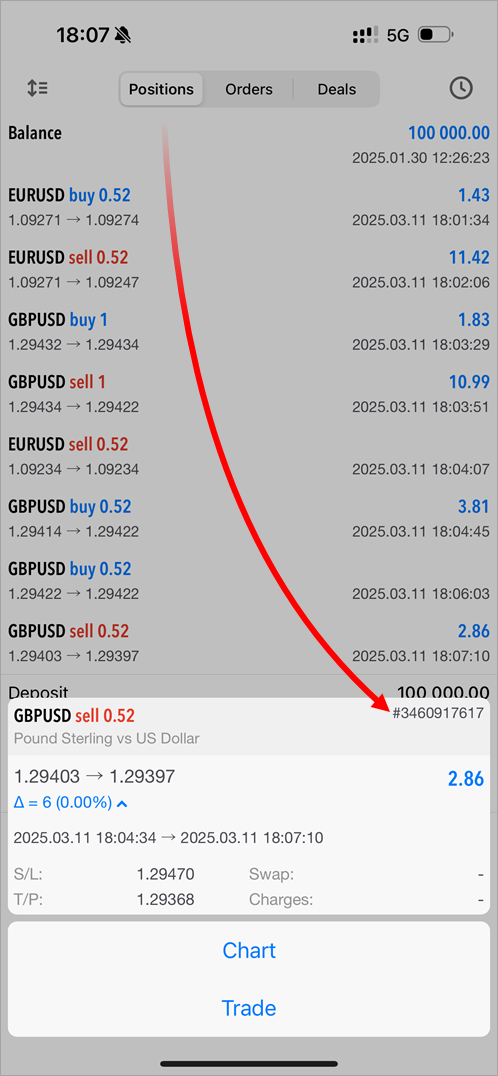
- Added display of position tickets in trading history.
- Improved quote delay indication if such a delay is used for a trading instrument. This information is now displayed on the chart, while the icon in the Market Watch section has been made more prominent.
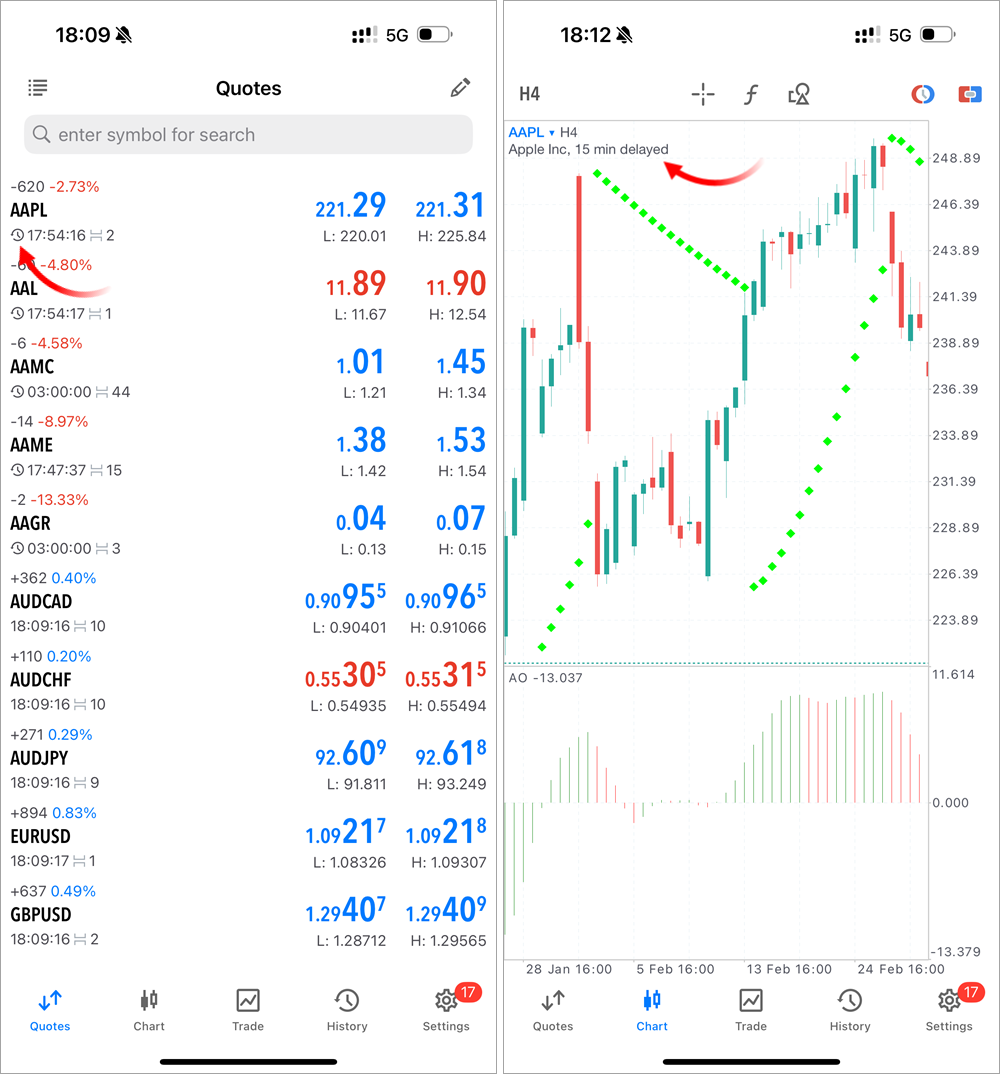
- Added support for new providers in the integrated payment system.
- Added field for entering date of birth when opening demo accounts.
- Improved chats: Fixed avatar display issues, added a document viewer, enabled support for *.webp images, and improved search functionality.
Download the latest version of the app and enhance your trading experience:
 |
This update fixes an error in the calculation of triple swaps in the strategy tester, which occurred under certain combinations of testing conditions. Additionally, a number of minor enhancements and fixes have been implemented to further improve the platform stability.
Terminal
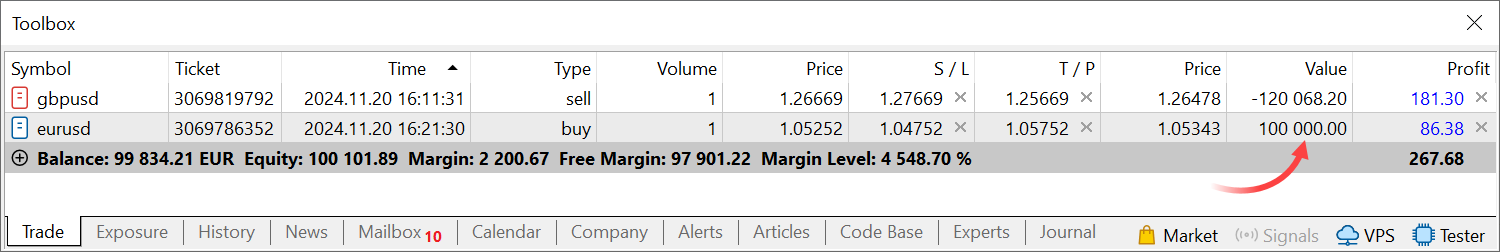
- Terminal: Changed
calculations for the position, order and deal values. The value is now
displayed in the account deposit currency rather than the base currency
of the trading symbol:
- Terminal: Added field for entering date of birth when opening demo accounts.
- Terminal: Fixed scaling of indicators displayed in the chart subwindow. For some oscillators, the minimum and maximum scale values could previously be selected incorrectly.
- Terminal: Optimized and accelerated unpacking of tick data and price history, which will increase the chart loading speed.
- Terminal: Fixed text color editing in the internal email compose window.
- Terminal: Updated user interface translations.
MQL5
- Added new OpenBLAS methods:
- EigenSolver2 – compute generalized eigenvalues and eigenvectors for a pair of ordinary square matrices (lapack function GGEV).
- EigenSolverX – compute eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a regular square matrix in Expert mode, i.e. with the ability to influence the computation algorithm and the ability to obtain accompanying computation data (lapack function GEEVX).
- EigenSolver2X – compute eigenvalues and eigenvectors for a pair of regular square matrices in Expert mode, i.e. with the ability to influence the computation algorithm and the ability to obtain accompanying computation data (lapack function GGEVX).
- EigenSolverShur – compute eigenvalues, the upper triangular matrix in Schur form, and the matrix of Schur vectors (lapack function GEES).
- EigenSolver2Shur – compute eigenvalues, generalized eigenvectors, generalized Schur forms, and left and right Schur vectors for a pair of regular square matrices (lapack function GGES).
- EigenSolver2Blocked – compute generalized eigenvalues and eigenvectors for a pair of regular square matrices using a block algorithm (lapack function GGEV3).
- EigenSolver2ShurBlocked – for a pair of regular square matrices, compute eigenvalues, generalized eigenvectors, generalized Schur forms, and left and right Schur vectors using a block algorithm (lapack function GGES3).
- EigenSymmetricRobust – compute eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a symmetric or Hermitian (complex conjugate) matrix using the Multiple Relatively Robust Representations, MRRR algorithm (lapack functions SYEVR, HEEVR).
- EigenSymmetricBisect – compute eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a symmetric or Hermitian (complex conjugate) matrix using the bisection algorithm (lapack functions SYEVX, HEEVX).
- Added new methods for complex matrices:
- TransposeConjugate – create a conjugate-transposed matrix.
matrix<complex<T>> matrix<complex<T>>::TransposeConjugate(void) const;
The method returns a new conjugate-transposed matrix in which the elements of the original matrix are transposed and converted to their complex conjugates.
If an error occurs, an empty matrix is returned. Use the GetLastError function to get the error code.
- CompareEqual – absolute comparison of two matrices.
int matrix<T>::CompareEqual(const matrix<T>& mat) const
The return values are:
- -1 – if the element of matrix A is less than the corresponding element of matrix B.
- 0 – if all elements of matrices A and B are identical.
- 1 – if the element of matrix A is greater than the corresponding element of matrix B.
The method can also return errors if the input data is invalid. To get the error code, use the GetLastError function.
- TransposeConjugate – create a conjugate-transposed matrix.
- Added Python support up to version 3.13 for the corresponding integration package. To update the package, run the following command:
pip install --upgrade MetaTrader5
- Fixed skipping of the first Timer event. An error occurred if a timer was started within the OnTimer handler.
MetaEditor
- Fixed calculation of values for input variables in the debugger mode. In some cases, the message "unknown identifier" was displayed instead of the value.
Tester
- Fixed search for required cross rates for currency conversion when testing applications using exchange instruments.
Web Terminal
- Added support for the Request execution type for large-volume orders.
- Added support for an extended description of the reason for requests rejected by a broker.
- Fixed account opening form. Information is now requested according to the broker settings.
- Fixed country detection during the registration of demo accounts.
- Fixed alignment in the dialog displaying the one-click trading warning.
Terminal
- Fixed an error that caused an incomplete tick history to be returned under certain conditions.
- Fixed autocompletion when selecting symbols in languages other than English. When you type a symbol name in the search field, the system automatically suggests relevant options based on the entered characters. The search function now works correctly and case-insensitively across all locales.
MQL5
- Descriptions of new OpenBLAS methods have been added to MQL5 Documentation. Currently, 15 new methods for matrices and vectors are available, with more to be added soon.
OpenBLAS is an efficient open-source solution for high-performance computing, especially when working with big datasets.Function
Action
Singular Value Decomposition, divide-and-conquer algorithm; considered the fastest among other SVD algorithms (lapack function GESDD).
Singular Value Decomposition, QR algorithm; considered a classical SVD algorithm (lapack function GESVD).
Singular Value Decomposition, QR with pivoting algorithm (lapack function GESVDQ).
Singular Value Decomposition, bisection algorithm (lapack function GESVDX).
Singular Value Decomposition, Jacobi high-level algorithm (lapack function GEJSV).
Singular Value Decomposition, Jacobi low-level algorithm (lapack function GESVJ). The method computes small singular values and their singular vectors with much greater accuracy than other SVD routines in certain cases.
Singular Value Decomposition, divide-and-conquer algorithm for bidiagonal matrices (lapack function BDSVDX).
Singular Value Decomposition, bisection algorithm for bidiagonal matrices (lapack function BDSVDX).
Compute eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a regular square matrix using the classical algorithm (lapack function GEEV).
Compute eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a symmetric or Hermitian (complex conjugate) matrix using the divide-and-conquer algorithm (lapack functions SYEVD, HEEVD).
A method function for calculating the relative contributions of spectral components based on their eigenvalues
A method function for calculating reconstructed and predicted data using spectral components of the input time series.
A method function for calculating reconstructed components of the input time series and their contributions.
A method function for calculating the reconstructed time series using the first component_count components.
- Fixed errors when running older versions of executable MQL5 program files (.ex5) that use matrix::CopyRates methods. These errors did not occur in files compiled under new versions.
- Fixed type-checking for orders allowed in union.
MetaTester
- Fixed crashes that could occur under certain conditions during the deinitialization of custom indicators.
Terminal
- Fixed crashes that could occur under certain conditions while stopping profiling of MQL5 programs.
MetaEditor
- Fixed memory leaks during MQL5 program compilation and when using intelligent code management functions.
MetaTester
- Fixed crashes that occurred under certain conditions when re-running single pass tests.
Terminal
- Restricted access to MQL5 trading and history functions if the account is subscribed to a signal.
When a signal subscription is detected on the account (regardless of whether copying is enabled in the current terminal), any MQL5 trading function calls are prohibited, including receiving open orders and positions, receiving history, and performing trading operations. A corresponding warning is logged in the journal:'XXX': signal subscription detected, trading and history access functions in MQL5 and Python disabledThe restrictions also apply to Python trading functions: positions_total, positions_get, orders_total, orders_get, history_orders_total, history_orders_get, history_deals_total, history_deals_get, order_check, and order_send.
If a signal subscription is canceled on the account or you connect to another account without a signal subscription, the restriction is lifted, and the following message is logged:'XXX': no signal subscription detected, trading and history access functions in MQL5 and Python enabledIf the restriction is active on the account, MQL5 functions will return the following response codes:
- OrderSend and OrderSendAsync return RET_REQUEST_AT_DISABLED_CLIENT
- OrdersTotal and PositionsTotal return 0
- PositionGetSymbol, PositionSelect, PositionSelectByTicket, and PositionGetTicket return ERR_MQLAPI_TRADE_POSITION_NOT_FOUND
- OrderGetTicket and OrderSelect returns ERR_MQLAPI_TRADE_POSITION_NOT_FOUND
- HistorySelect returns ERR_MQLAPI_TRADE_DEAL_NOT_FOUND
- Fixed, optimized and accelerated tick history request and export to CSV\HTML files.
- Added Microsoft Edge WebView2 support for displaying HTML content in the trading platform on macOS.
Compared to the outdated MSHTML, the new component significantly
expands content displaying capabilities by providing access to modern
technologies. The transition to WebView2 improves the appearance of
Market, Signals, VPS, and other sections, increasing their performance
and creating more responsive interfaces.
- Fixed context menu in the internal mail sending window.
- Fixed filtering in the trading instrument selection dialog. It is no longer necessary to first input instrument names to hide expired instruments.
- Fixed calculation of margin requirements in the contract specification window. The error occurred for Exchange Stocks and Bonds instruments.
- Improved bulk position closing function for FIFO accounts. Incompatible operation types are no longer displayed for such accounts, including closing of all profitable/losing positions, same-directed positions and opposite positions.
- Fixed issue where users could not place opposite pending orders on accounts where position closing follows the FIFO rule.
- Fixed calculation of liquidation value for accounts with positions on Exchange Futures instruments.
- Fixed floating profit calculations for positions on Exchange Bonds and Exchange MOEX Bonds instruments.
- Disabled automatic demo account creation when the platform is launched without previously added accounts.
- Improved name and email validation when registering accounts.
- Fixed margin calculation for hedged positions. The error could occur in certain cases when using floating margin on the account (calculated based on the volume/value of current positions).
- Fixed updating the "Next" button state in the demo account opening
dialog. After entering the phone or email confirmation code, the button
could remain inactive under certain conditions.
- Updated user interface translations.
MQL5
- Added native integration with the OpenBLAS matrix computation library.
OpenBLAS is a high-performance open-source linear algebra library that implements BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms) and some LAPACK functions. OpenBLAS is designed to improve computational performance, particularly in matrix and vector operations, which are often used in scientific and engineering tasks such as machine learning, numerical methods, and simulations.
Key features of OpenBLAS:- Multithreading support: OpenBLAS can efficiently use multiple processor cores for parallel computations, significantly accelerating operations on multiprocessor systems.
- Optimization for processor architectures: OpenBLAS includes optimized builds for various processors such as Intel, AMD, ARM and others. The library automatically detects processor characteristics (supported instruction sets like AVX/AVX2/AVX512) and selects the most suitable function implementations.
- Extensive BLAS operation support: OpenBLAS implements core BLAS functions, including vector operations (e.g., vector addition and dot product), matrix operations (multiplication), and vector-matrix operations.
- LAPACK compatibility: The library supports LAPACK (Linear Algebra PACKage) functions for more complex linear algebra operations, such as solving systems of linear equations, calculating matrix eigenvalues, and others.
- High performance: Compared to other BLAS libraries, OpenBLAS often demonstrates better results due to hand-crafted optimizations for specific processor architectures.
OpenBLAS is widely used in applications involving numerical computations:- Training neural networks and other machine learning tasks.
- Scientific computing (e.g. modeling of physical processes).
- Processing and analyzing large amounts of data.
The following methods are currently available in MQL5:
Singular value decomposition:- SingularValueDecompositionDC – divide-and-conquer algorithm; considered the fastest among other SVD algorithms (lapack function GESDD).
- SingularValueDecompositionQR – QR algorithm; considered a classical SVD algorithm (lapack function GESVD).
- SingularValueDecompositionQRPivot – QR with pivoting algorithm (lapack function GESVDQ).
- SingularValueDecompositionBisect – bisection algorithm (lapack function GESVDX).
- SingularValueDecompositionJacobiHigh – Jacobi high level algorithm (lapack function GEJSV).
- SingularValueDecompositionJacobiLow – Jacobi low level algorithm (lapack function GESVJ). The method computes small singular values and their singular vectors with much greater accuracy than other SVD routines in certain cases.
- SingularValueDecompositionBidiagDC – divide-and-conquer algorithm for bidiagonal matrices (lapack function BDSVDX).
- SingularValueDecompositionBidiagBisect – bisection algorithm for bidiagonal matrices (lapack function BDSVDX).
- EigenSolver – compute eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a regular square matrix using the classical algorithm (lapack function GEEV).
- EigenSymmetricDC – compute eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a symmetric or Hermitian (complex conjugate) matrix using the divide-and-conquer algorithm (lapack functions SYEVD, HEEVD).
Detailed documentation will be provided soon.
- Added the SYMBOL_SWAP_MODE_CURRENCY_PROFIT value in the ENUM_SYMBOL_SWAP_MODE enumeration. If the SymbolInfoInteger function returns this value, swaps on the account are charged in the profit calculation currency.
- Expanded ONNX Runtime support. Added new types of machine learning operations, allowing you to run more advanced neural models.
- We continue transition to a more efficient MQL5 compiler, which is already used for some functions. The transition will allow for further optimizations and faster program execution.
- Added new data types to support the OpenBLAS library:
- complexf – complex number represented by float data
- vectorcf – vector containing elements of type complexf
- matrixcf – matrix containing elements of type complexf
- Improved WebRequest operations when working with websites that violate URL formatting rules, contain redirect errors or have long lists of alternative DNS names.
- Fixed simultaneous assignment of matrix or vector types to multiple variables.
MetaEditor
- Updated available models for the AI Assistant. The more advanced GPT-4o mini now replaces GPT-3.5 Turbo. Also added the 01-mini model.
- Fixed debugger error due to which variable values could fail to update in the watch window.
- Updated user interface translations.
MetaTester
- Fixed saving of margin coefficients in custom symbol settings.
- Fixed memory leaks that could occur between testing passes under certain conditions.
Web Terminal
- Added Crosshair mode for viewing precise values and measuring distances on charts.
Enable the mode by clicking the relevant button on the left panel. Move the crosshair over any point on the chart to see the date and price on the respective axes. To measure distance, click on any point on the chart and drag the cursor to another point while holding the mouse button.
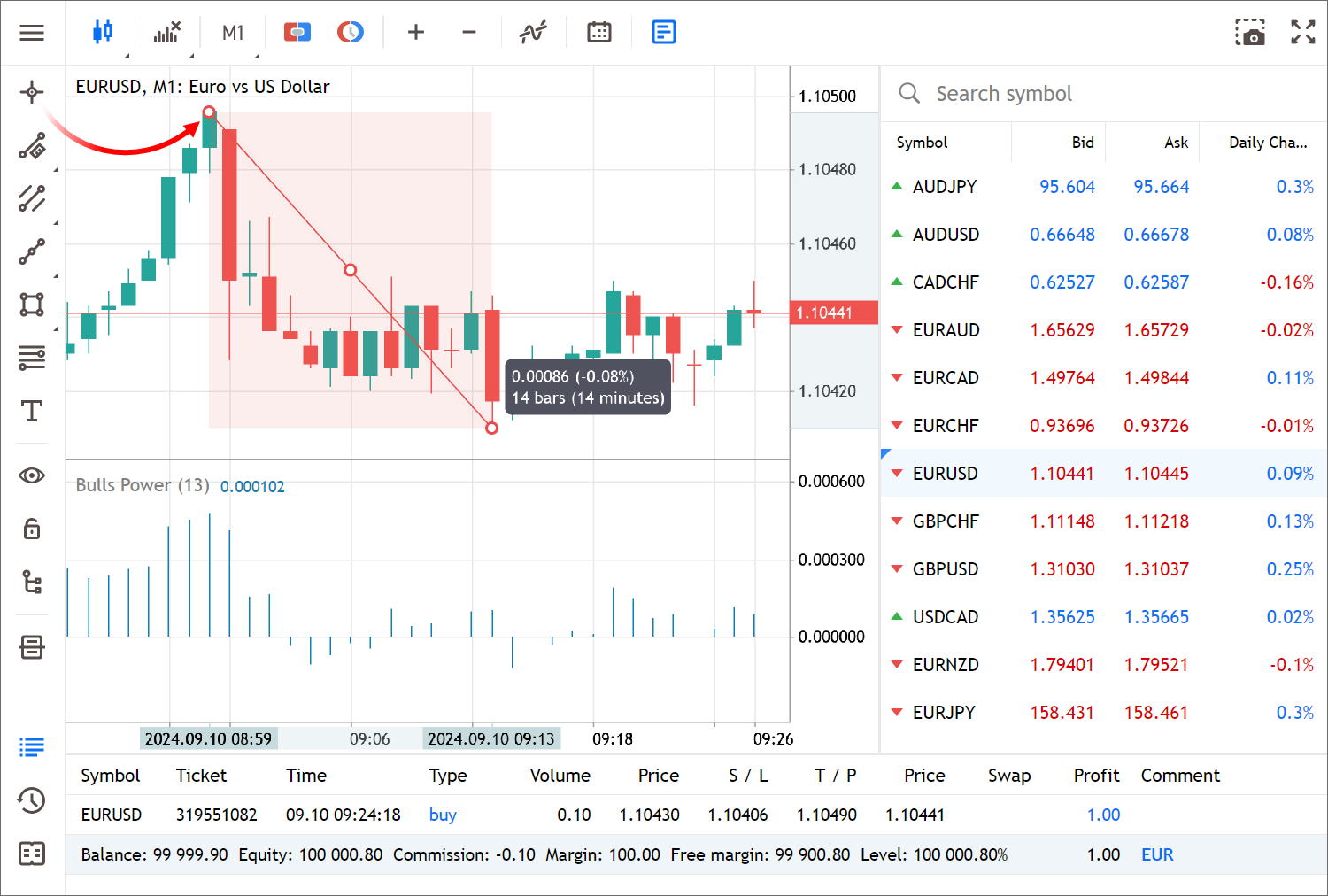
You can also use shortcuts: press the middle mouse button to enable crosshair and use Esc or right-click to disable it.
- Added a simple line chart constructed on bar closing prices:
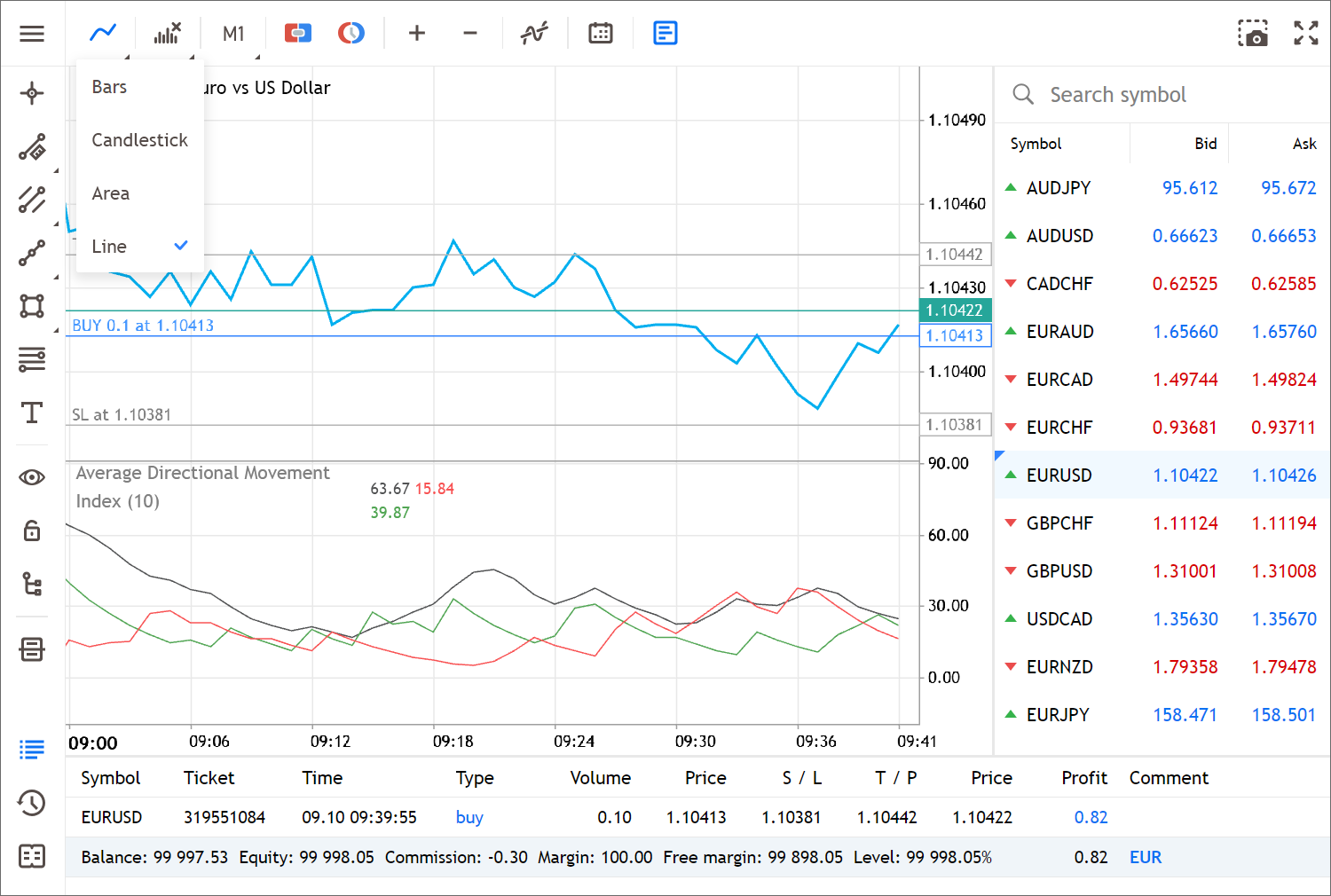
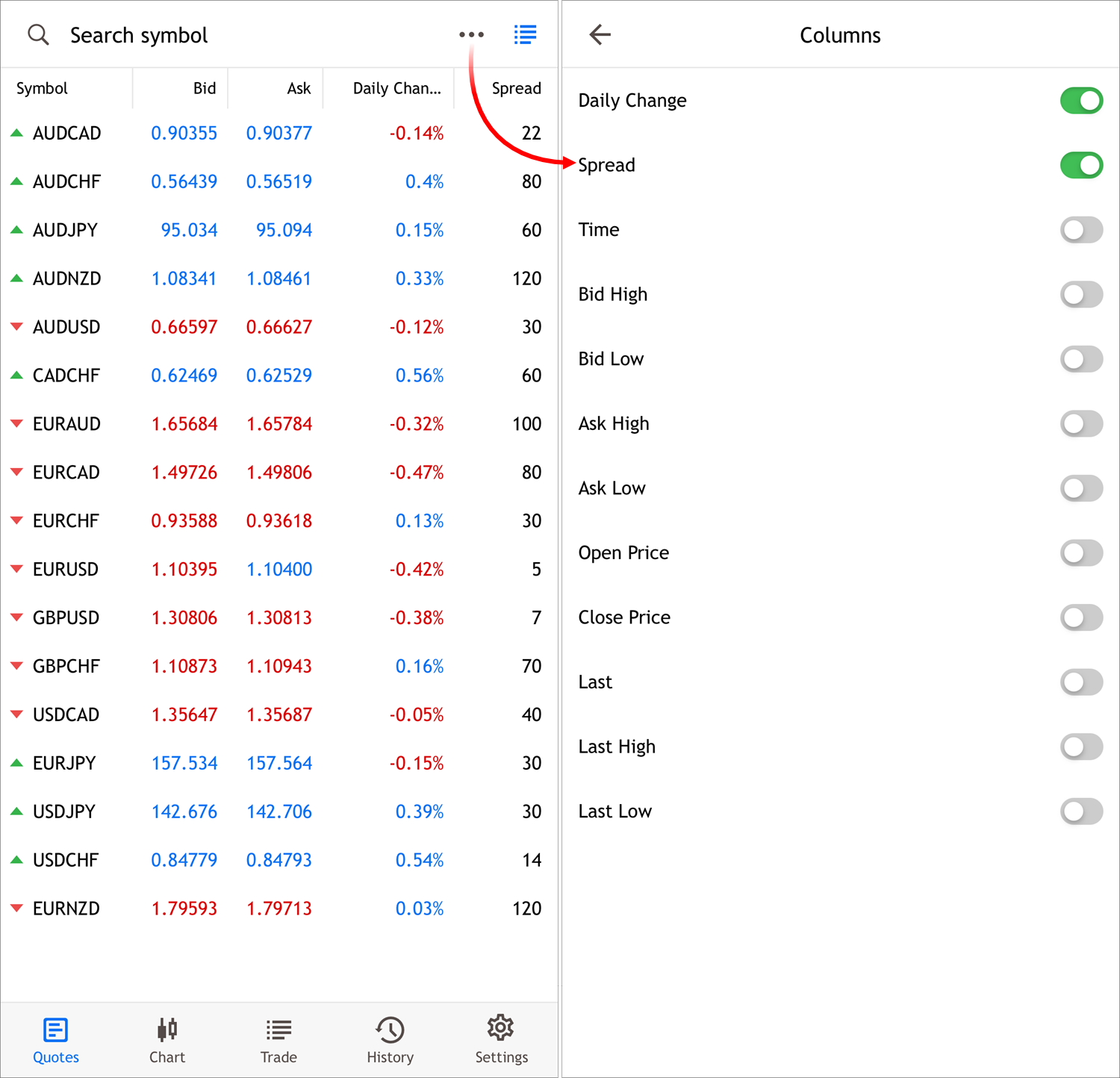
- In the mobile view, added ability to display additional columns in
the Market Watch section. To configure, switch to the table mode and
click "...":
- Added hotkeys:
- Home – scroll to the beginning of the chart (earliest date)
- End – scroll to the end of the chart (latest date)
- Page Up – scroll the chart one screen back
- Page Down – scroll the chart one screen forward
- Enhanced data security for account connection storage.
- Improved chart scrolling, dragging, and scaling functionality.
- Accelerated initial loading of the web platform on the page.
- Optimized loading of bars.
- Fixed floating profit calculations for positions on Exchange Bonds and Exchange MOEX Bonds instruments.
- Fixed volume input on the one-click trading panel on charts.
- Fixed error in updating the order volumes in the Depth of Market. Values could have been delayed in updating under certain conditions.
- Fixed minimum allowable trading volume check when placing orders.
- Fixed margin calculation for hedged positions. The error could occur in certain cases when using floating margin on the account (calculated based on the volume/value of current positions).
- Fixed error where the Buy and Sell buttons on the one-click trading panel could become inactive until the volume was changed.
Terminal
- Fixed terminal crash, which could occur upon testing start under certain conditions.
MQL5
- Fixed operation of the MQL_PROGRAM_NAME property for service applications. The property could return an incorrect service instance.
Web Terminal
- Fixed validation of browser compatibility with the web terminal. In some cases, users might have erroneously received a message indicating that their browser was not supported.
- Fixed opening of demo accounts.
- Minor fixes and improvements.
The update will be available through the Live Update system.
MetaTrader 5 Android
- Completely
redesigned interface for the tablet versions. It now features a modern
design, already proven on the iOS and web versions of the platform. The
main sections are now located at the bottom of the screen, and chart
operation commands appear are available on the left.
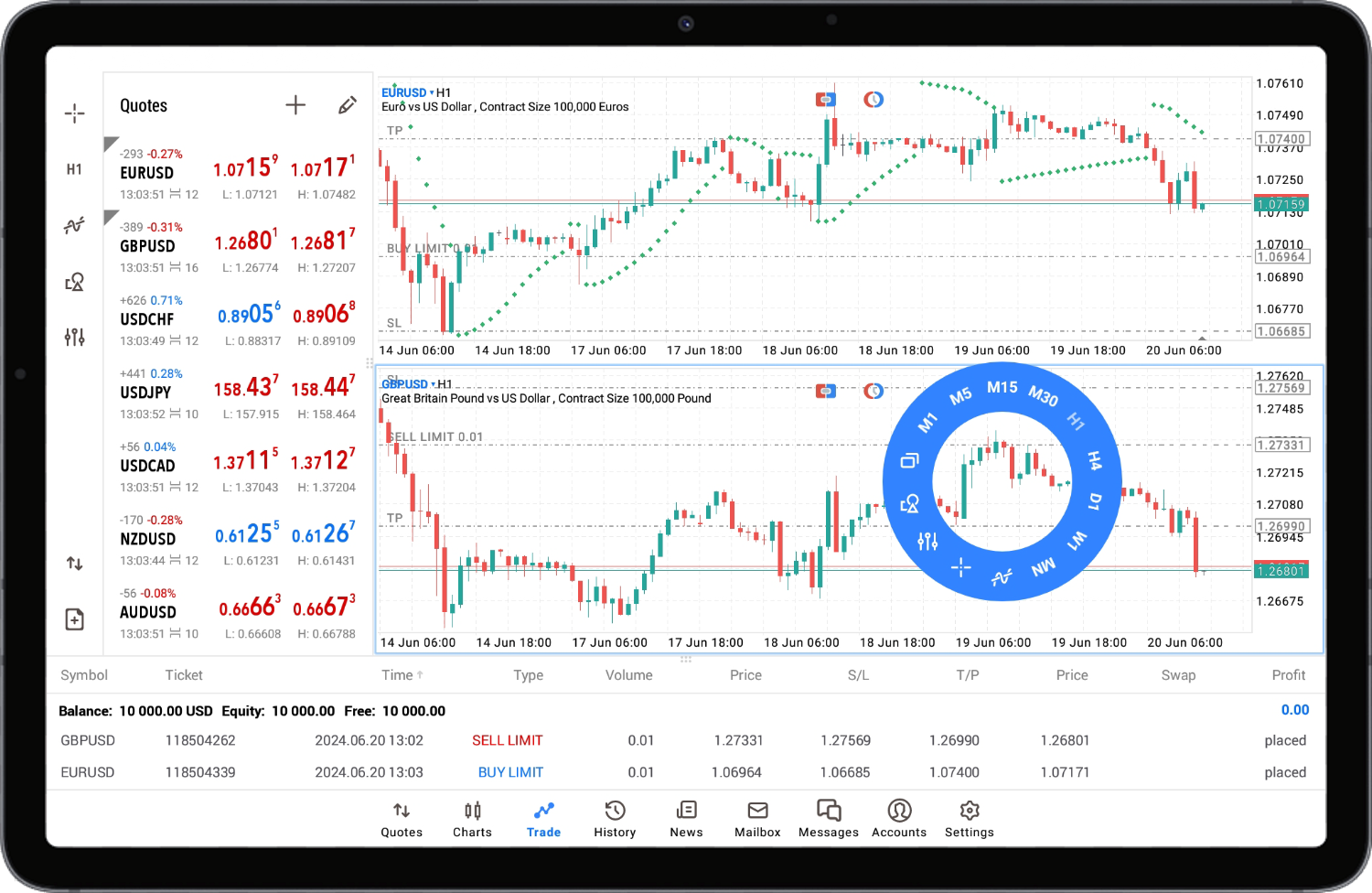
- Added context menu to the position history section, allowing quick access to the trading dialog or chart of the corresponding symbol.
- Hidden command switching to the trading dialog for non-tradable symbols.
- Fixed operation with the MetaQuotes-Demo server.
Update your mobile apps through Google Play, Huawei AppGallery or by downloading the APK file.
Terminal
- Fixed errors which could cause incorrect operation of the Live Update system under certain conditions.
- Added new hotkey, Alt+X, to open a list of Expert Advisors.
- Fixed errors reported in crash logs.
MetaTester
- Fixed errors in setting certain properties of the Bitmap graphic object.
- The connection of testing agents to the MQL5 Cloud Network is now prohibited when operating in virtual environments and when the processor does not support the AVX instruction set.
Web Terminal
- Fixed error in the operation of the one click trading panel on the chart.
- Fixed warning dialog that opens when you enable the one click trading panel on the chart.
MetaEditor
- Added Welcome page to assist users in starting their journey with algorithmic trading and application development.
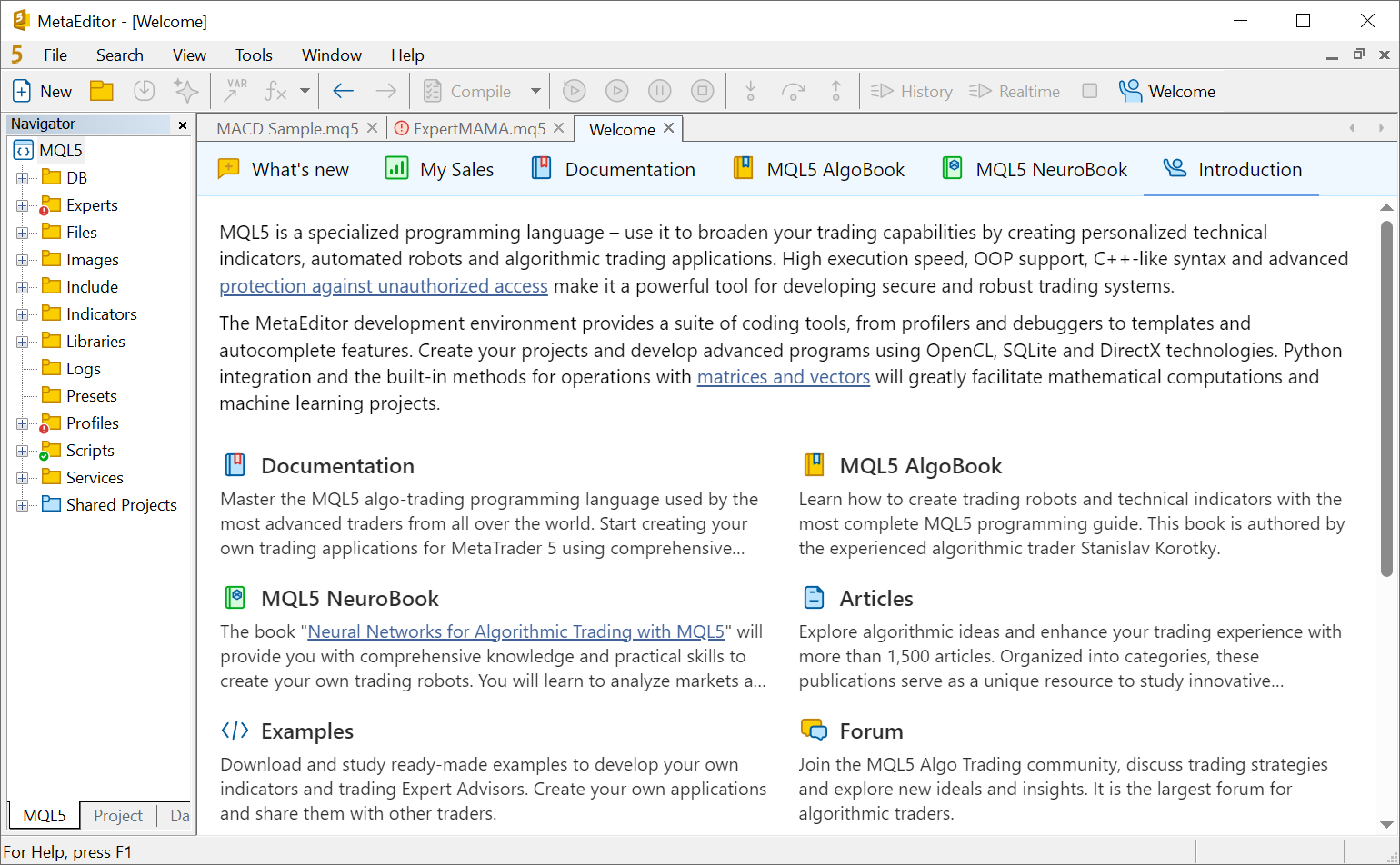
Materials for beginners
The "Introduction" section presents educational materials available on MQL5.com: language documentation, books, articles, developer forums and code base library. It also introduces services where you can apply and monetize your knowledge: the applications market, freelance and trading signals.
In the documentation and books sections, you can find a more detailed description of the available learning materials.
Useful features for developers
The "What's New" section offers a collection of essential information to keep developers up-to-date:
- Latest trading and development forum discussions
- New Freelance orders
- Latest articles on application development
- Newly added publications in the CodeBase source code library
Additionally, you will find here a list of recently opened files for quick access.
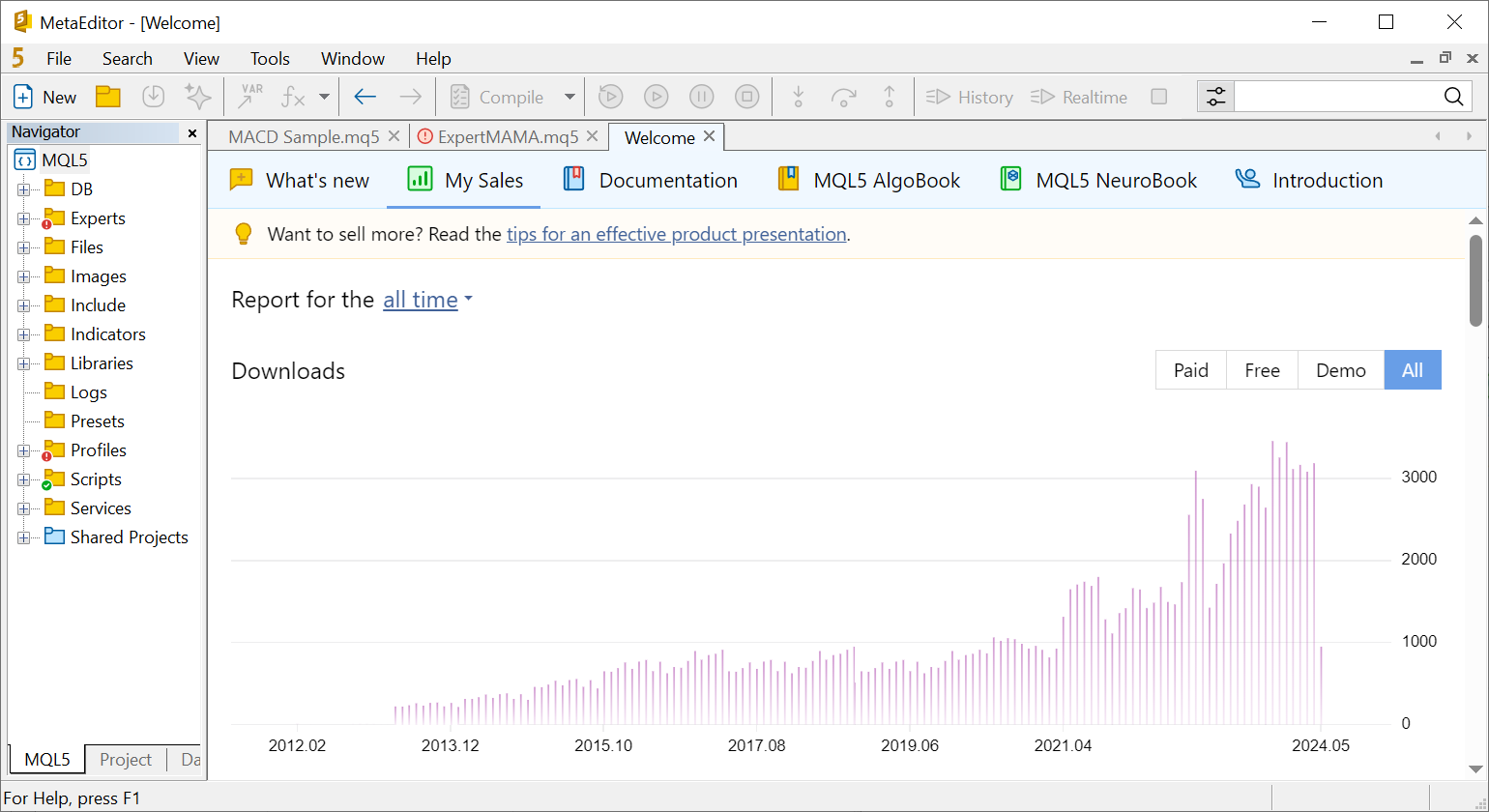
For users actively selling their applications in the Market, the "My Sales" report offers an invaluable tool for assessing their performance. It provides access to:
- Comprehensive sales and download statistics over time.
- Sales geography, offering insights into regions where your products have the highest popularity. This can suggest ideas for further project expansion, such as localization into specific languages or targeted advertising campaigns in particular regions.
- Data on top-selling products based on sales volume and revenue generated. The graph can be filtered based on license type: full or rental for a certain duration. Additionally, you can see here a graph with product price changes. All of this will help you understand your customers.
- Detailed download and sales statistics for each product.
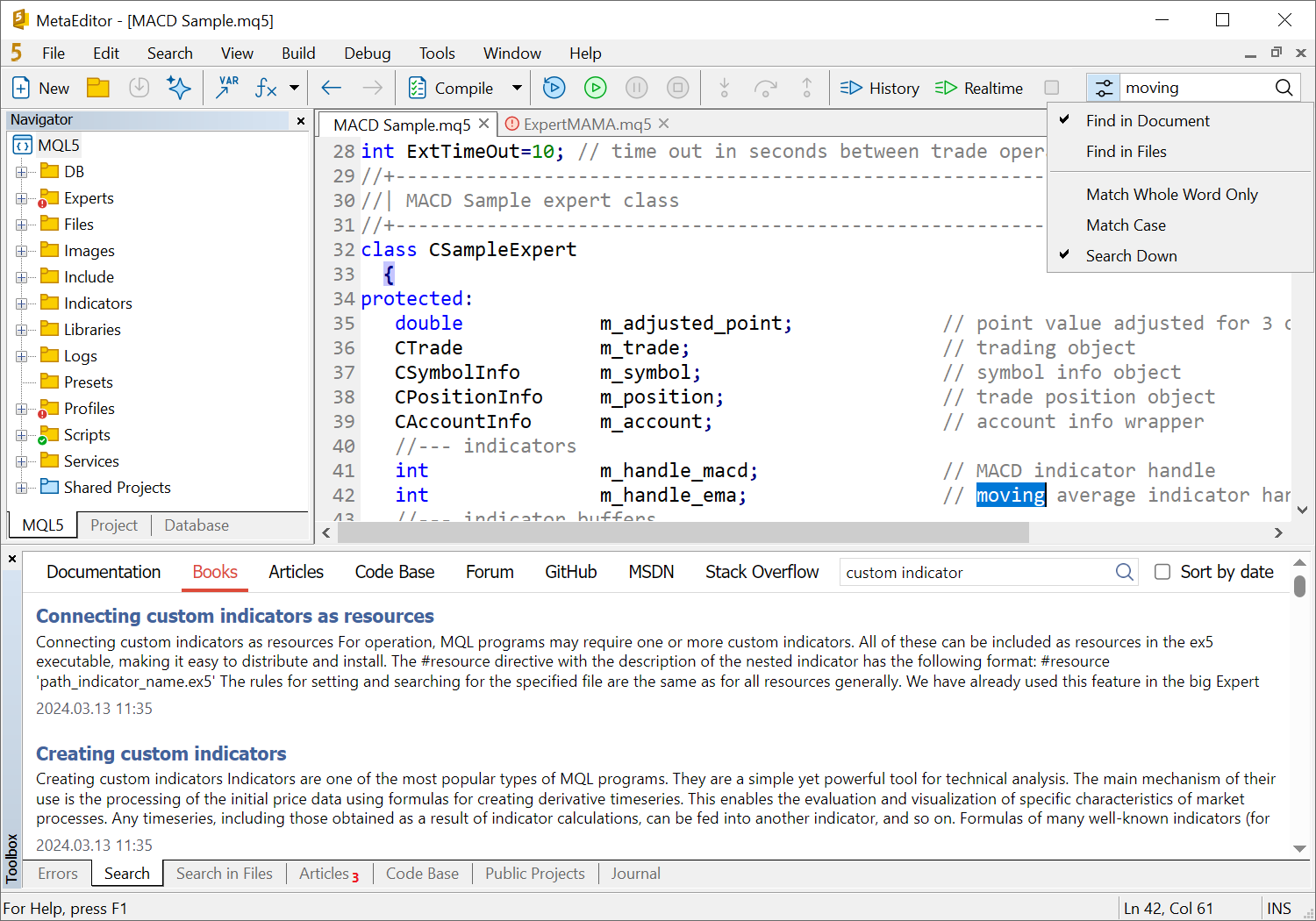
- Improved built-in search. The top search bar is now used exclusively for searching text within the current document or in local files. For a global search through educational materials and codes, use a separate section in the Toolbox.
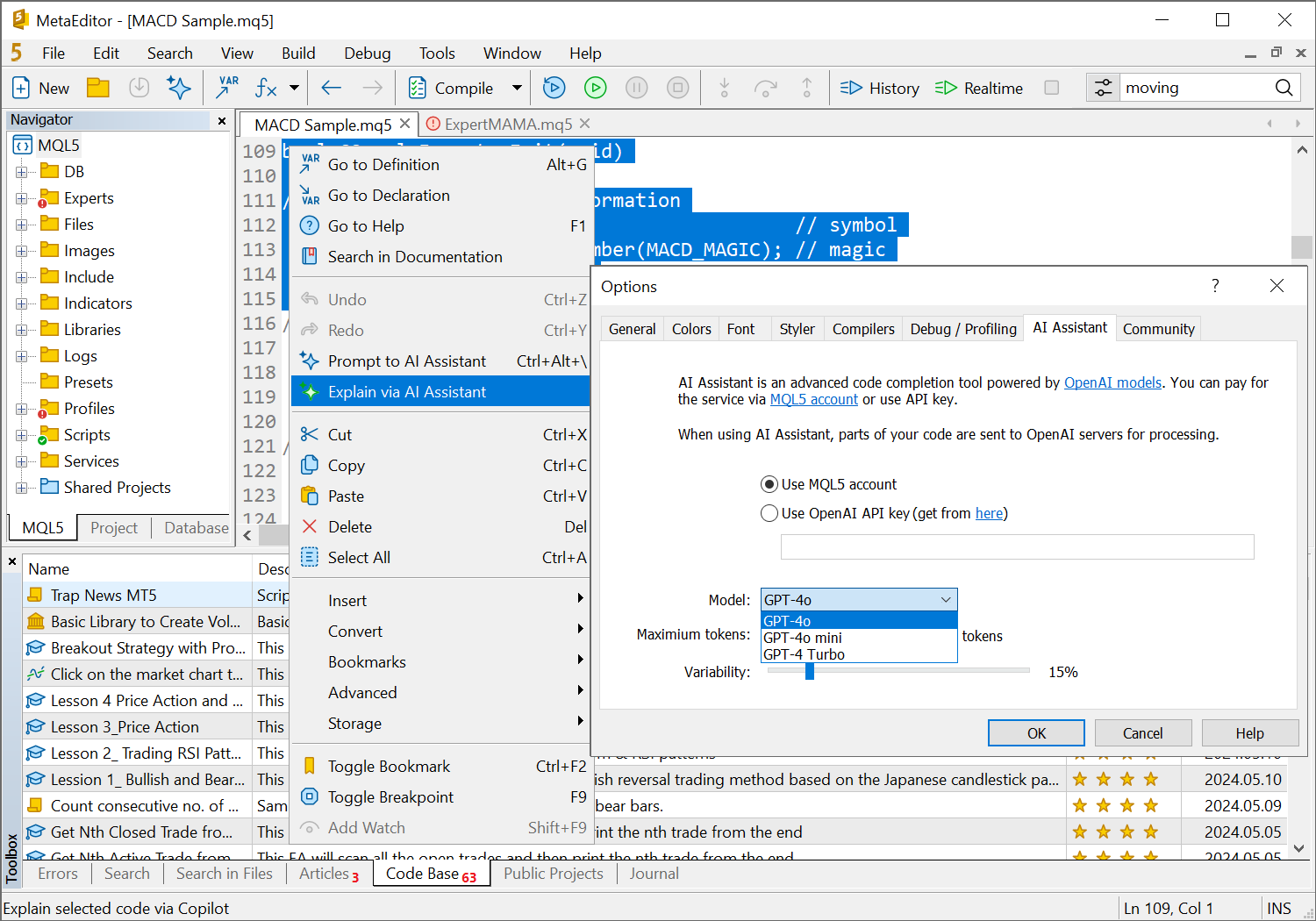
- Added support for GPT-4o, the latest ChatGPT model, in AI Assistant. It can be used to automatically complete code and get hints. You can select the new model in the MetaEditor settings.
- Updated user interface translations.
Terminal
- Increased precision in displaying the calculation price in the trading instrument specification.
- Added the hotkey Alt+X to open the list of Expert Advisors.
- Fixed MFE and MAE calculations in the trading report.
- Fixed saving and restoring of economic calendar filtering settings by country and currency.
- Fixed application of templates to charts. Now, if the display of trading history is enabled for the chart, the corresponding objects will not disappear after applying a template.
- Fixed errors in the options board. The addition of symbols to the board could cause the platform to freeze under certain conditions.
- Fixed error in the position editing dialog. In some cases, incorrect levels could be entered instead of the current Stop Loss and Take Profit values.
- Updated user interface translations.
MQL5
- Optimized and accelerated the ArrayResize function. The function can be executed up to 40% faster under certain conditions.
- Updated support for ONNX.
- Fixed MessageBox function calls in service applications. Regardless of the button pressed by the user in the dialog, the function returned a null value.
- Fixed error that, in some cases, caused incomplete initialization of MQL5 programs.
- Fixed error parsing some macros. The error occurred when using a large number of constants.
MetaTrader 5 Web Terminal
- Extended list of available analytical objects. Now, you can utilize the ruler to measure time and prices, draw shapes (rectangle, ellipse, triangle, and circle), and add labels to your charts. All objects can be found in the left panel:
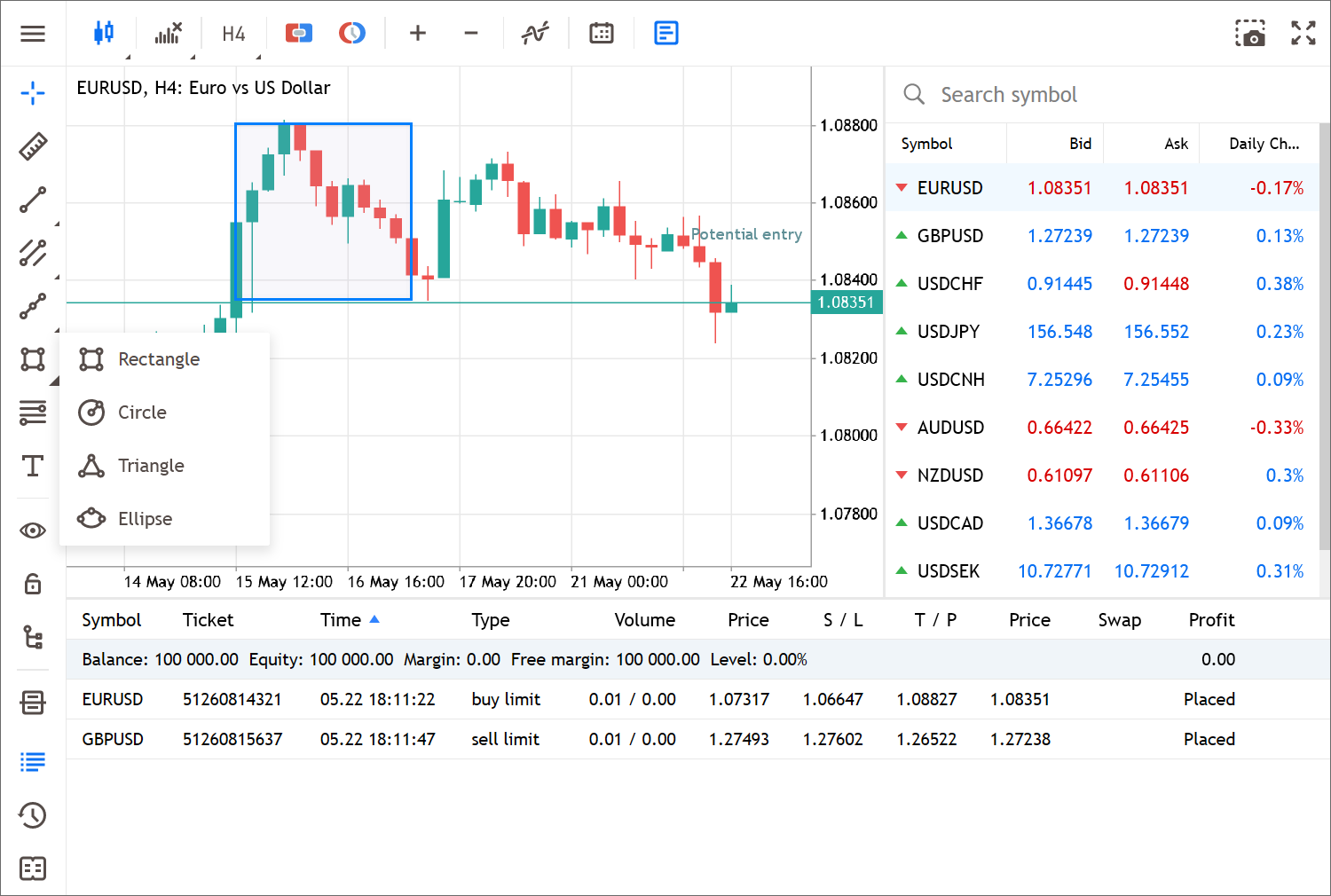
- Added ability to rename objects.
- Improved integration with the economic calendar. Optimized and accelerated data requests.
- Accelerated chart operations.
- Accelerated application start and connection to a trading account.
- Fixed setting that controls the display of trading operations on the chart.
- Fixed display of margin requirements in contract specifications.
- Fixed display of account statuses in the history section. Issues could occur on devices with narrow screens.
- Fixed display of the Depth of Market changes.
Terminal
- Fixed errors in subscribing to free products in the Subscriptions service. The relevant button might not be displayed in the dialog under certain conditions.
- Updated translations of the user interface.
MQL5
- Expanded support for keyboard events:
- Added CHARTEVENT_KEYUP event for the OnChartEvent handler. It allows the tracking of events related to key releases.
- Added processing of Dead keys. These are the keys that modify the appearance of the character generated by the key struck immediately after. For example, in the Greek layout, a stressed vowel ά, έ, ύ, etc., can be generated by first pressing ";" and then the vowel. The pressing of such keys can be tracked using the TranslateKey function.
- Improved TranslateKey and TerminalInfoInteger functions. Now, when receiving CHARTEVENT_KEYUP or CHARTEVENT_KEYDOWN events in OnChartEvent, you can obtain the complete keyboard state at the time the event occurred. For example, if the user pressed the Z key, you will be able to determine whether the Ctrl or Shift key was pressed at that moment. For other events, the functions will continue to operate as before, returning the keyboard state at the current moment.
-
Updated the Alglib library. Following the update, the following methods
in the CMatrixDouble and CMatrixComplex classes have been modified:
vector<double/complex> operator[](const int i) const; vector<double/complex> operator[](const ulong i) const;
They have been replaced by a single method with a constant return value:
const vector<double/complex> operator[](const ulong i) const;
This modification will assist in capturing incorrect use of the result in place as in the new Alglib version, the code mat[row][col]=x operates differently from the old version. Previously, this indicated writing to a matrix. Now, the value is written to a temporary object vector<double/complex>, which is immediately destroyed after recording.
Adding const to the return value enables the use of mat[row][col]=x. Because mat[row] now returns a constant vector, attempting to overwrite its element with mat[row][col] will result in a compilation error.
- Fixed error that could cause the incorrect operation of ChartGet* functions under certain conditions.
MetaEditor
- Added search through the contents of the book Neural Networks for Algorithmic Trading in MQL5. The new option appears in the same section as the previously published book MQL5 Programming for Traders.
Tester
- Fixed optimization when using a large number of remote agents. In some cases, the error could cause excessive CPU usage.
MetaTrader 5 Web Terminal
- Fixed setting of limit orders for instruments with the exchange execution mode. Now, when the price of the order being placed changes relative to the current price (becomes higher or lower), the order type will not switch from Buy Limit to Sell Limit and vice versa, as it does for instruments of other types. Thus, users can place Buy Limit orders above the market and Sell Limit orders below the market, ensuring that the transaction price is guaranteed to be limited.
- Fixed the display of selected symbol counters in the Market Watch.
Terminal
- Added 28
new Expert Advisors and 12 new indicators to the standard platform
package. The applications are available in the Expert Advisors\Free
Robots and Indicators\Free Indicators sections in the Navigator. Each
program is available as source code with detailed comments to assist you
in learning the MQL5 language.
The robots implement trading strategies based on technical indicators and candlestick patterns, such as 3 Black Crows – 3 White Soldiers, Bullish Engulfing – Bearish Engulfing, Bullish Harami – Bearish Harami and others. New indicators are implementations of popular channels: Camarilla, DeMark, Donchian, Fibonacci and Keltner, among others.
- Preparations are underway for the launch of Nasdaq market data subscriptions. Right from the platform, traders will be
able to access real-time quotes and deep price histories for hundreds of
financial instruments from one of the largest exchanges. Subscriptions
will be available to any user having a demo account on the
MetaQuotes-Demo server and an MQL5.community account.
To get started, you only need to purchase a subscription and add the relevant symbols to your Market Watch. You can use these symbols as regular instruments: open charts, analyze them using objects and indicators, and run Expert Advisors in the strategy tester. Access to all information is implemented as for ordinary financial instruments with which you work with a broker.
- Improved
margin section in the instrument specification. The section now features
margin rates and calculated values for each instrument.
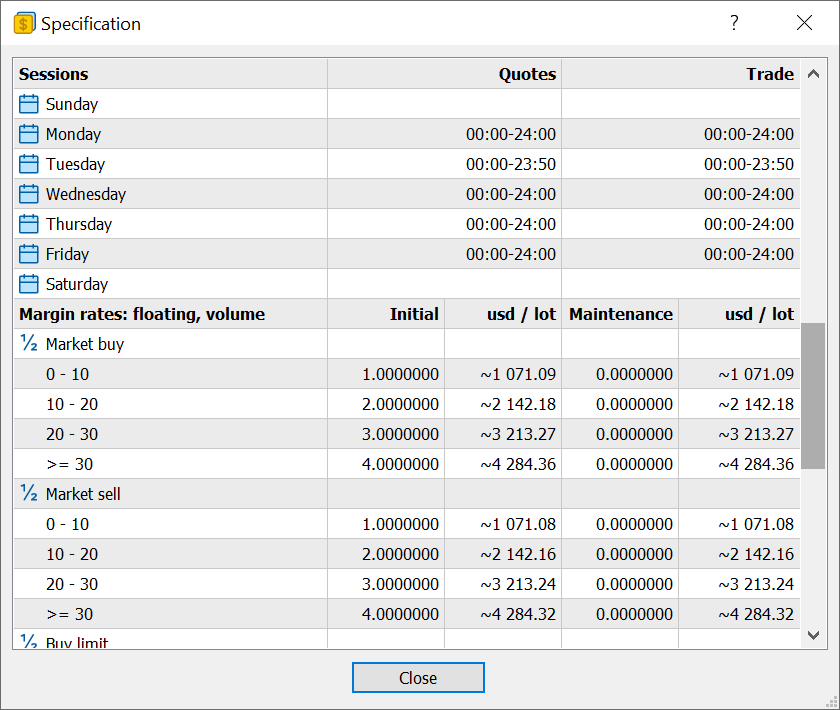
Fixed errors in margin display for certain types of symbols.
- Added link to the MQL5 Telegram channel in the Help menu. Interesting content for developers is regularly shared in the channel, including reviews of new programming articles and free robots and indicators from the Code Base. Subscribe to the channel and ensure you don't miss out on important information.
- Added support for the ShutdownTerminal parameter in the [StartUp] section of custom configuration files. Use this parameter to launch the platform to execute one-off tasks using scripts. For example, you have a script that takes a screenshot of the chart. You can create a configuration file that launches this script along with the platform. If you add ShutdownTerminal set to 'Yes' to this file, the platform will automatically shut down immediately after the script completes.
- Enhanced protection of network protocols and Market products.
- Disabled support for the Signals service for demo accounts. To access enhanced statistics on your training accounts, use the new trading report. It features a plethora of metrics characterizing your strategy profitability and risks, including growth, balance and equity graphs, diagrams of trade distribution by direction and instruments, and much more.
- Fixed display of broker agreement links in the Help menu.
- Improved selection of the best server when renting VPSs.
- Fixed refreshing of the subscriptions page when switching between sections in the Navigator.
- Fixed updating of the list of agreements when opening a preliminary account.
- Updated translations of the user interface.
MQL5
- Added MQL_STARTED_FROM_CONFIG property in the ENUM_MQL_INFO_INTEGER enumeration. Returns true if the script/Expert Advisor was launched from the StartUp section of the configuration file. This means that the script/Expert Advisor had been specified in the configuration file with which the terminal was launched.
- We continue expanding support for ONNX models.
Machine learning tasks do not always require greater computational accuracy. To speed up calculations, some models use lower-precision data types such as Float16 and even Float8. To allow users to input the relevant data into models, the following functions have been added to MQL5:
bool ArrayToFP16(ushort &dst_array[],const float &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayToFP16(ushort &dst_array[],const double &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayToFP8(uchar &dst_array[],const float &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayToFP8(uchar &dst_array[],const double &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP16(float &dst_array[],const ushort &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP16(double &dst_array[],const ushort &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP8(float &dst_array[],const uchar &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP8(double &dst_array[],const uchar &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt);
Since real number formats for 16 and 8 bits may differ, the "fmt" parameter in the conversion functions must indicate which number format needs to be processed. For 16-bit versions, the new enumeration NUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT is used, which currently has the following values:
- FLOAT_FP16 – standard 16-bit format also referred to as half.
- FLOAT_BFP16 – special brain float point format.
For 8-bit versions, the new ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT enumeration is used, which currently has the following values:
- FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FN
– 8-bit floating point number, 4 bits for the exponent and 3 bits for
the mantissa. Typically used as coefficients.
- FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FNUZ — 8-bit floating point number, 4 bits for the exponent and 3 bits for the mantissa. Supports NaN, does not support negative zero and Inf. Typically used as coefficients.
- FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FN – 8-bit
floating point number, 5 bits for the exponent and 2 bits for the
mantissa. Supports NaN and Inf. Typically used for gradients.
- FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FNUZ — 8-bit floating point number, 5 bits for the exponent and 2 bits for the mantissa. Supports NaN, does not support negative zero and Inf. Also used for gradients.
- FLOAT_FP16 – standard 16-bit format also referred to as half.
- Added new matrix and vector methods used in machine learning:
- PrecisionRecall computes values to construct a precision-recall curve. Similarly to ClassificationScore, this method is applied to a vector of true values.
- ReceiverOperatingCharacteristic — computes values to construct the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve. Similarly to ClassificationScore, this method is applied to a vector of true values.
- ONNX Runtime updated to version 1.17. For release details, please see GitHub.
- Python integration package updated to version 5.0.4200, added support for Python 3.12. Update your package using the command "pip install --upgrade MetaTrader5" to get the latest changes.
- Added DEAL_REASON_CORPORATE_ACTION property in the ENUM_DEAL_REASON enumeration. It indicates a deal executed as a result of a corporate action: merging or renaming a security, transferring a client to another account, etc.
- Added support for comparing complex vectors and matrices for the Compare method. The comparison involves estimating the distance between complex numbers. The distance is calculated as sqrt(pow(r1-r2, 2) + pow(i1-i2, 2) and is a real number that can already be compared with epsilon.
- Fixed conversion of color type variables to text in RGB format.
- Fixed returning of the result of obtaining eigenvectors in the Eig method in the case of a complex eigenvalue. Added method overload for complex evaluation.
- Fixed OrderCalcMargin function operation for certain cases.
MetaEditor
- Added link to the recently released book "MQL5 Programming for Traders"
in the Help\MQL5.community menu. The book has also been added to the
search system, and thus you can find the necessary information directly
from MetaEditor:
- Built-in search improvements:
- The search results section in the Toolbox window has been divided into two tabs: "Search" for online search results (documentation, articles, book, etc.) and "Search in files" for local results.
- A separate
search string has been added to the results section. You can use it
instead of the search bar in the main MetaEditor toolbar.
- Added support for AVX, AVX2 and AVX512 modes when compiling commands from the command line. To compile, add one of the following keys to your command: /avx, /avx2 or /avx512.
- SQLite engine for database operations updated to version 3.45.
- Disabled support for Internet Explorer. Now only Microsoft Edge WebView2 is used to display HTML pages. Compared to the outdated MSHTML, the new component significantly expands content displaying capabilities by providing access to the latest technologies. The use of WebView2 improves the appearance of some MetaEditor sections, increases performance, and creates a more responsive interface.
- Fixed freezing that occurred in rare cases on function autocompletion.
Tester
- Fixed calculations of triple swaps if the test start day falls on the triple-swap day.
MetaTrader 5 Web Terminal
Improved display of margin requirements in contract specifications. Now, in addition to ratios and initial parameters for calculations, specifications display the final margin values. If the margin amount depends on the position volume, the corresponding levels will be shown in the dialog.
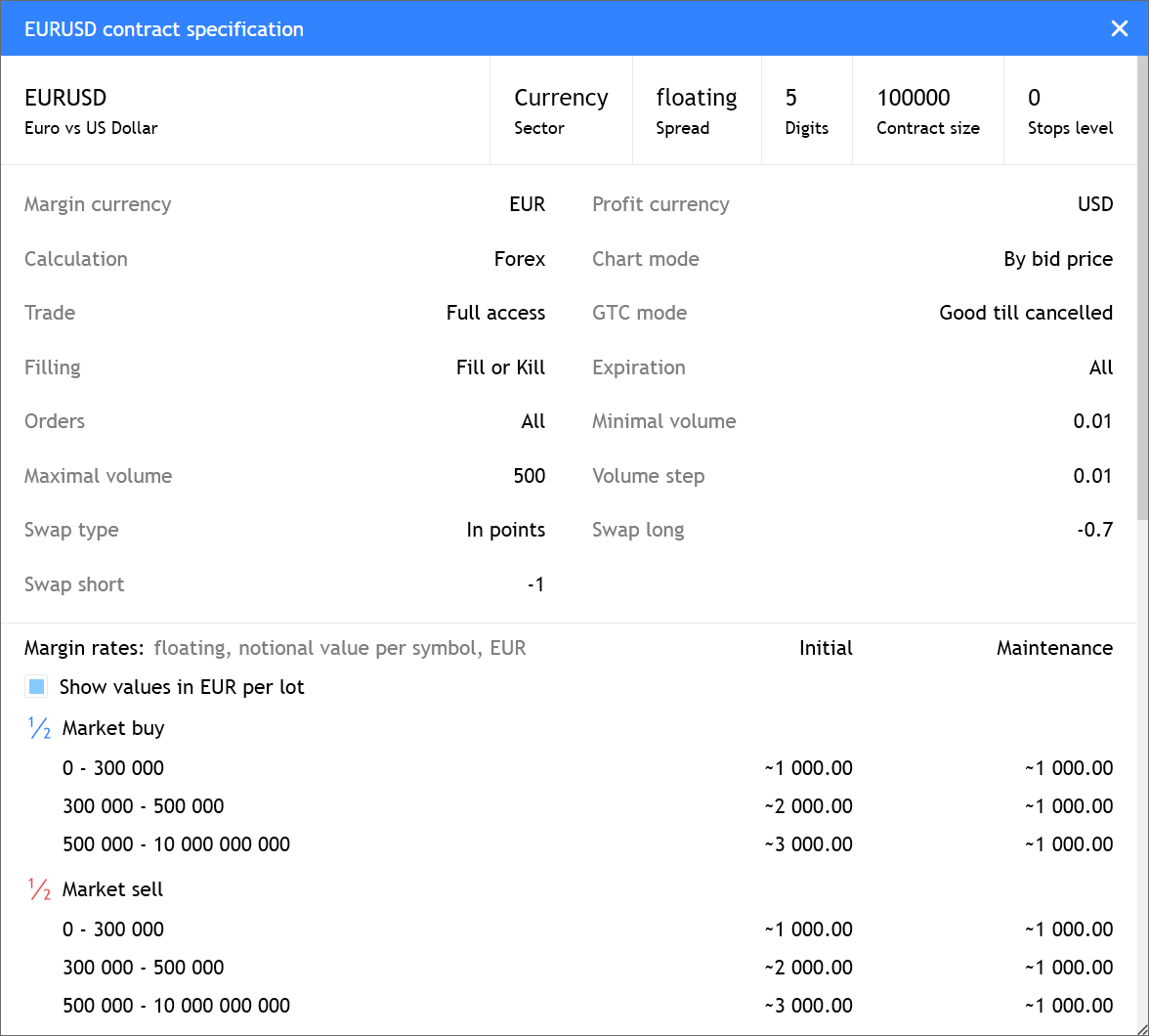
The margin is calculated based on the instrument price at the time the specification window opens and is not updated in real time. Therefore, the values should be considered indicative. To recalculate values based on current prices, reopen the instrument specification.
Terminal
- Added export of trading reports to HTML and PDF files. With this option, you can easily share your
trading achievements with colleagues and investors. New export commands
are available in the File menu and in the report menu.
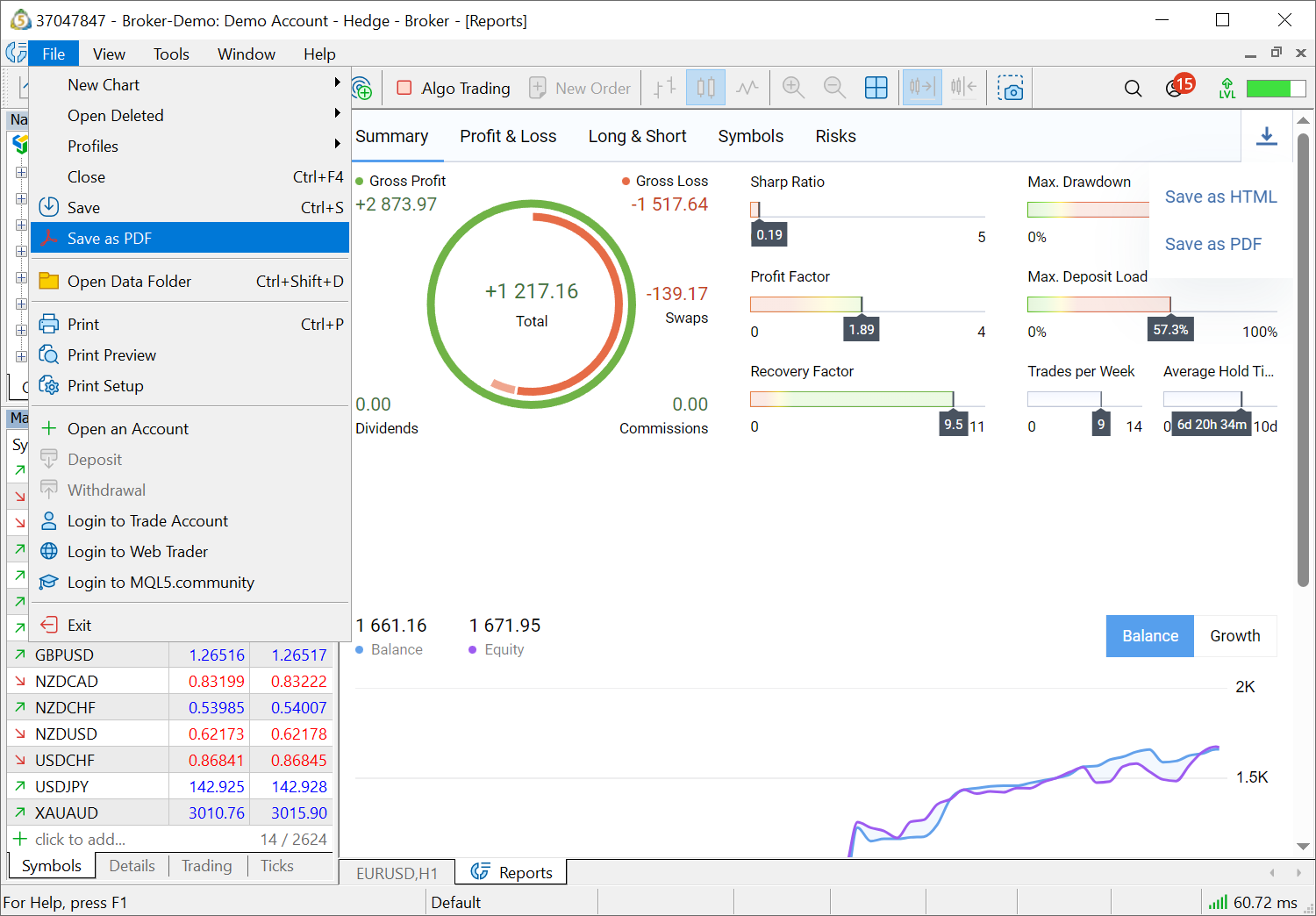
- Added ability to save the current state of the Market Watch window to a CSV file. To do this, select Export in the context menu.
The file will save the metrics that are selected at the time of export.
To save more data, enable additional columns through the context menu.
- Improved display of margin requirements in contract specifications.
Now, instead of ratios and initial parameters for calculations,
specifications display the final margin values. If the margin amount
depends on the position volume, the corresponding levels will be shown
in the dialog.
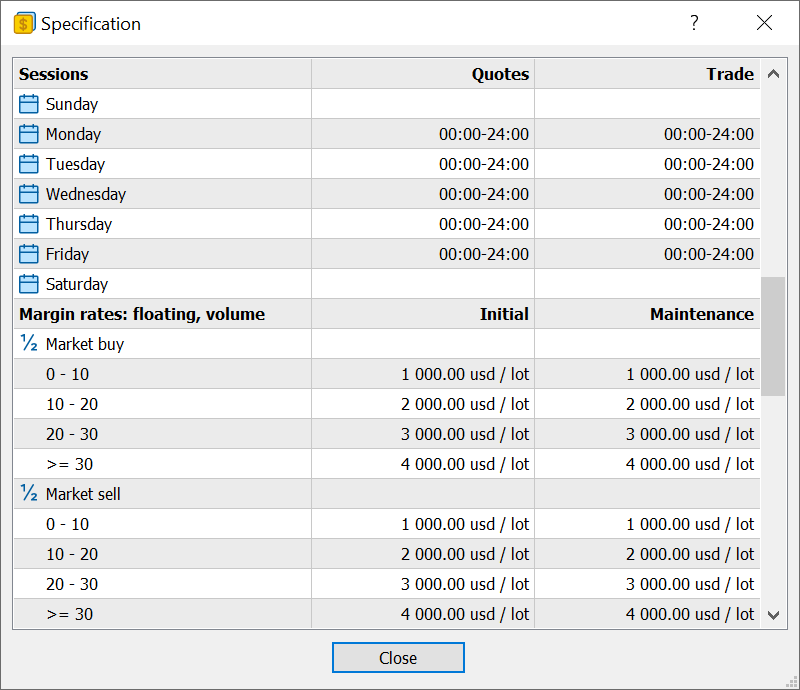
The margin is calculated based on the instrument price at the time the specification window opens and is not updated in real-time. Therefore, the values should be considered indicative. To recalculate values based on current prices, reopen the instrument specification.
- Disabled support for the Signals service for demo accounts. To access enhanced statistics on your training accounts, use the new trading report.
It features a plethora of metrics characterizing your strategy
profitability and risks, including growth, balance and equity graphs,
diagrams of trade distribution by direction and instruments, and much
more.
- Fixed display of the potential profit/loss value when editing Take Profit and Stop Loss for Stop Limit orders.
- Fixes and improvements related to the operation of the Payment system.
- Fixed duplicate checks when loading a set of symbols in the Market Watch from a *.set file.
- Fixed web installer for Parallels. Now, when using this virtualization
system on macOS with M1/M2/M3, the platform will be installed correctly.
- Updated user interface translations.
- Fixed errors reported in crash logs.
MQL5
- Added new methods for operations with matrices and vectors, which are utilized in Machine Learning.
- ConfusionMatrix — computes the error matrix. The method is applied to a vector of predicted values.
- ConfusionMatrixMultilabel — computes the error matrix for each label. The method is applied to a vector of predicted values.
- ClassificationMetric — computes the classification metric to evaluate the quality of the predicted data compared to the true data. The method is applied to a vector of predicted values.
- ClassificationScore — computes the classification metric to evaluate the quality of the predicted data compared to the true data.
- Fixed data saving to a text file in the UTF-8 format using the FileWrite function.
- Disabled and deprecated Signal* functions. They will now return empty signal sets.
MetaEditor
- Increased sampling rate for profiling. The profiler now captures application states 10,000 times per second, enabling more accurate measurement of function execution rates.
- Updated available models in the automatic coding AI assistant. Added ChatGPT-4 Turbo model, removed outdated implementations.
- Fixed errors when replacing words in a selected text fragment.
Tester
- Fixed forward testing freezing, which could occur in generic optimization mode.
- Optimized and accelerated operations with the trading history from MQL5 programs.
- Fixed profit calculations for Close By operations. An error could occur for trading instruments not matching the main testing symbol.
Web Terminal
- Fixed update of trading symbol properties upon the relevant property changes on the broker's side.
- Fixed display of candlestick bodies on the chart. The chart could fail to display small bodies.
- Fixed operation of the Country field in the account opening form.
Terminal
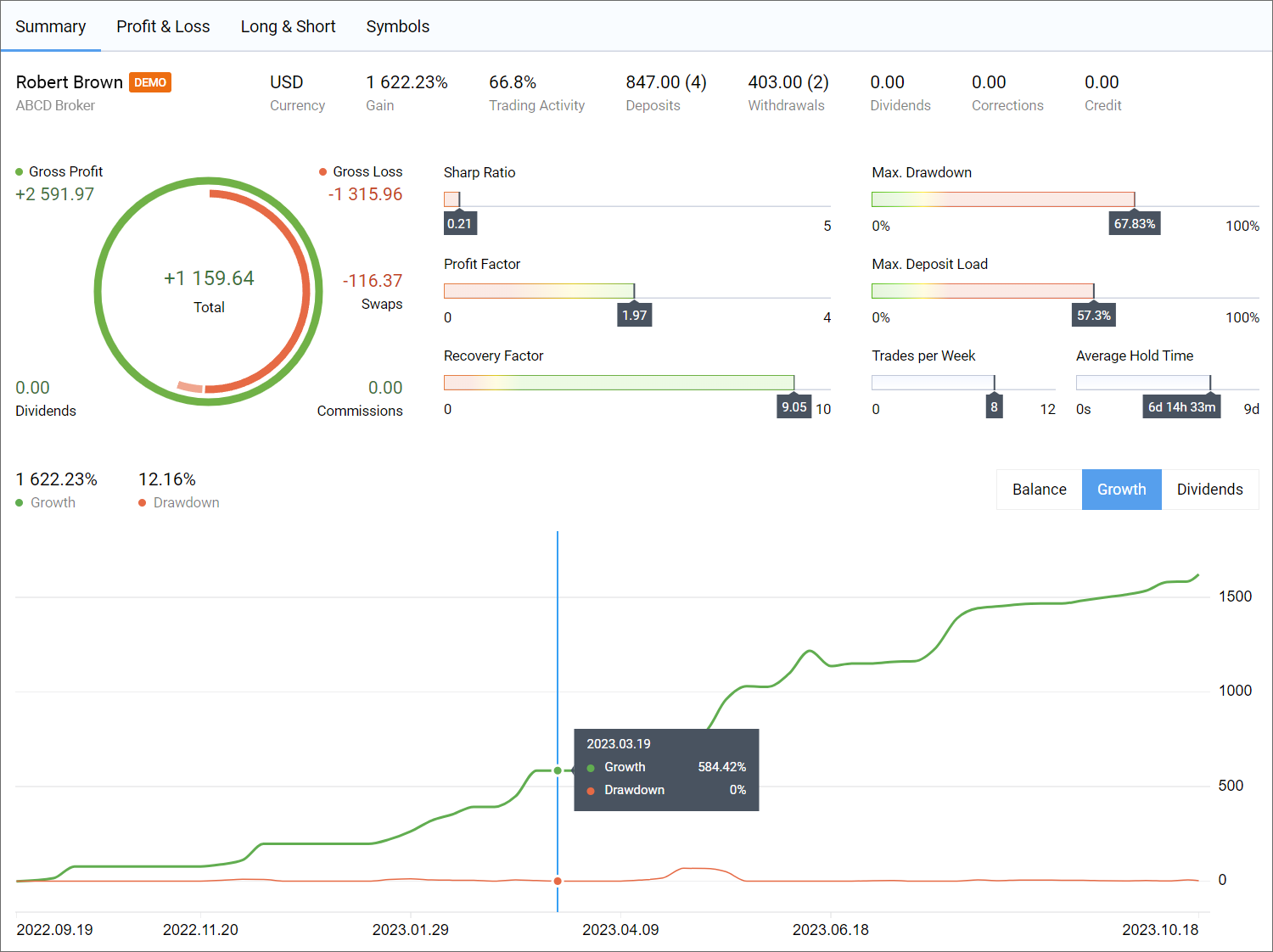
- New trading report improvements. Fixed display of the first value on the growth graph and drawdown calculations.
-
When opening accounts, traders receive several messages through the
internal email system. They provide credentials and useful information
about the platform capabilities and built-in services. We have updated
and enhanced these emails, translated them into 50 languages, and
completely updated the design.
- Optimized account deposit and withdrawal pages.
- Fixed volume change error when placing a new order. With some combinations of trading instrument settings, the field was not available for editing.
- Fixed display of broker agreement links in the demo account opening dialog.
- Updated user interface translations.
MQL5
- Fixed an error that could cause the MQL5 program to crash at startup under certain conditions.
MetaTrader 5 Web Terminal
- Fixed display of Stop Loss and Take Profit values in trading history.
- Enhanced logging. New log messages display information on successful and failed connections.
- Fixed context menu operation in the Market Watch.
- Fixed display of notifications about operation results when trading from the Depth of Market.
- Fixed error which caused the indicator subwindow to be removed from the chart when calling the trading dialog.
- Fixed on-chart dragging of trading levels displayed on top of analytical objects.
Terminal
- Added display of monthly funds growth in new trading reports. To view the metrics, go to the Summary report and select the Balance mode.
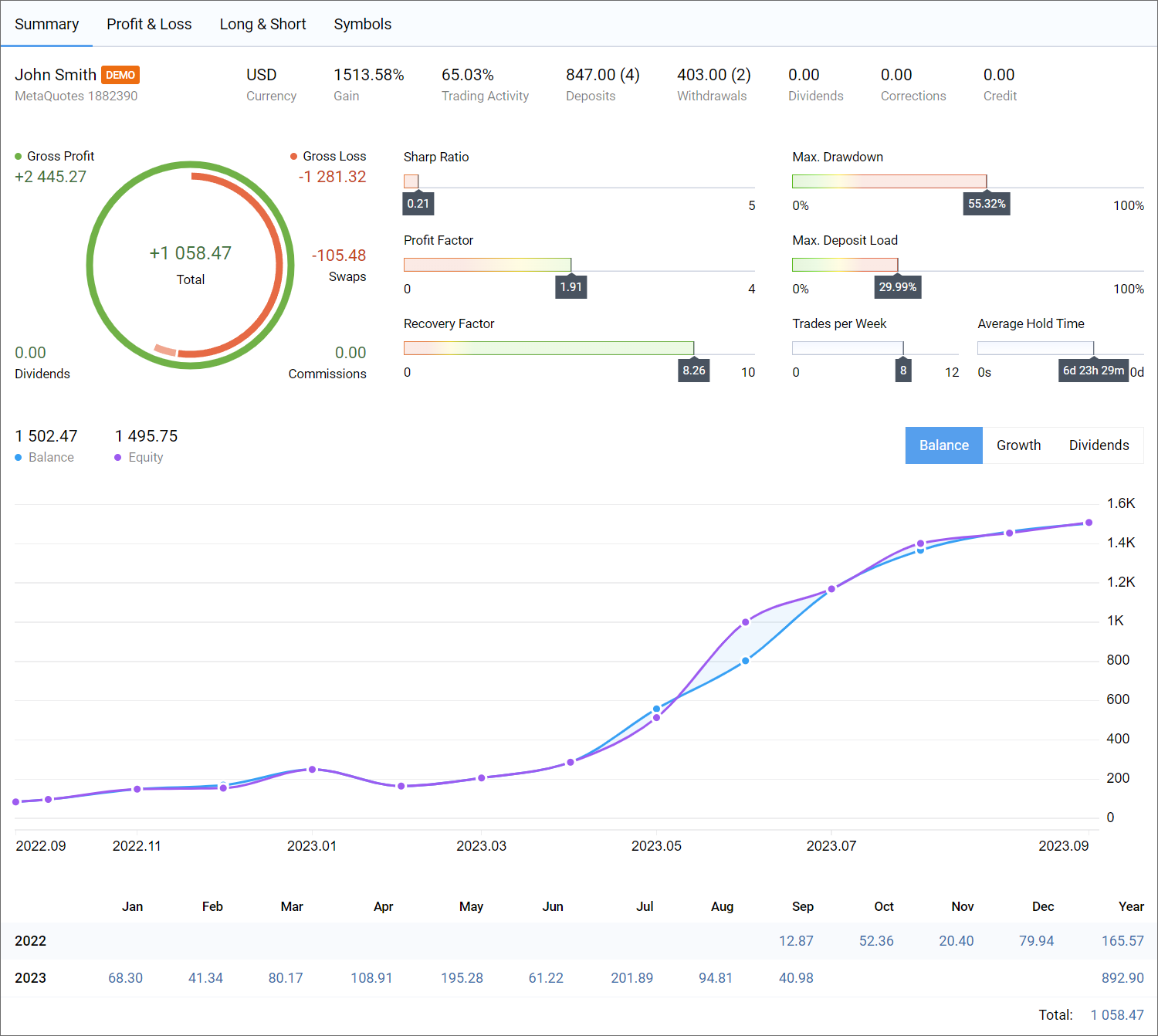
- Fixed and improved display of the new trading report.
- ONNX Runtime updated to version 1.16. For release details, see GitHub.
- Updated user interface translations.
MetaTrader 5 Web Terminal
- Fixed display of password change and account opening dialogs.
- Fixed display of Stop Loss and Take Profit values in history. An error could occur after the modification of the relevant levels.
- Added scroll in the risk warning dialog.
- Updated user interface translations.
- Other improvements and fixes.
Terminal
- New trading report improvements. Fixed the display of the total swaps value and the profit chart by symbols.
- Optimized deposit and withdrawal pages. For further details about the new platform integration with payment systems, please read the build 3950 release notes.
-
Optimized recalculations of financial operations across the entire
platform, including the strategy tester. Now profit, margins, and many
other parameters are calculated faster.
- Updated user interface translations.
MQL5
- Added Conjugate methods for complex, vector<complex> and matrix<complex> types. They implement complex conjugate operations.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { complex a=1+1i; complex b=a.Conjugate(); Print(a, " ", b); /* (1,1) (1,-1) */ vectorc va= {0.1+0.1i, 0.2+0.2i, 0.3+0.3i}; vectorc vb=va.Conjugate(); Print(va, " ", vb); /* [(0.1,0.1),(0.2,0.2),(0.3,0.3)] [(0.1,-0.1),(0.2,-0.2),(0.3,-0.3)] */ matrixc ma(2, 3); ma.Row(va, 0); ma.Row(vb, 1); matrixc mb=ma.Conjugate(); Print(ma); Print(mb); /* [[(0.1,0.1),(0.2,0.2),(0.3,0.3)] [(0.1,-0.1),(0.2,-0.2),(0.3,-0.3)]] [[(0.1,-0.1),(0.2,-0.2),(0.3,-0.3)] [(0.1,0.1),(0.2,0.2),(0.3,0.3)]] */ ma=mb.Transpose().Conjugate(); Print(ma); /* [[(0.1,0.1),(0.1,-0.1)] [(0.2,0.2),(0.2,-0.2)] [(0.3,0.3),(0.3,-0.3)]] */ }
- Added handing of ONNX model outputs of the 'Sequence of maps' type.
For ONNX models that provide Map sequences in the output layer (ONNX_TYPE_SEQUENCE of ONNX_TYPE_MAP), a dynamic or fixed array of structures should be passed as the output parameter. The first two fields of this structure must match the ONNX_TYPE_MAP key and value types and be fixed or dynamic arrays.
Consider the iris.onnx model created by the following Python script:
from sys import argv data_path=argv[0] last_index=data_path.rfind("\\")+1 data_path=data_path[0:last_index] from sklearn.datasets import load_iris iris_dataset = load_iris() from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris_dataset['data'], iris_dataset['target'], random_state=0) from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1) knn.fit(X_train, y_train) # Convert into ONNX format from skl2onnx import convert_sklearn from skl2onnx.common.data_types import FloatTensorType initial_type = [('float_input', FloatTensorType([None, 4]))] onx = convert_sklearn(knn, initial_types=initial_type) path = data_path+"iris.onnx" with open(path, "wb") as f: f.write(onx.SerializeToString())
Open the created onnx file in MetaEditor: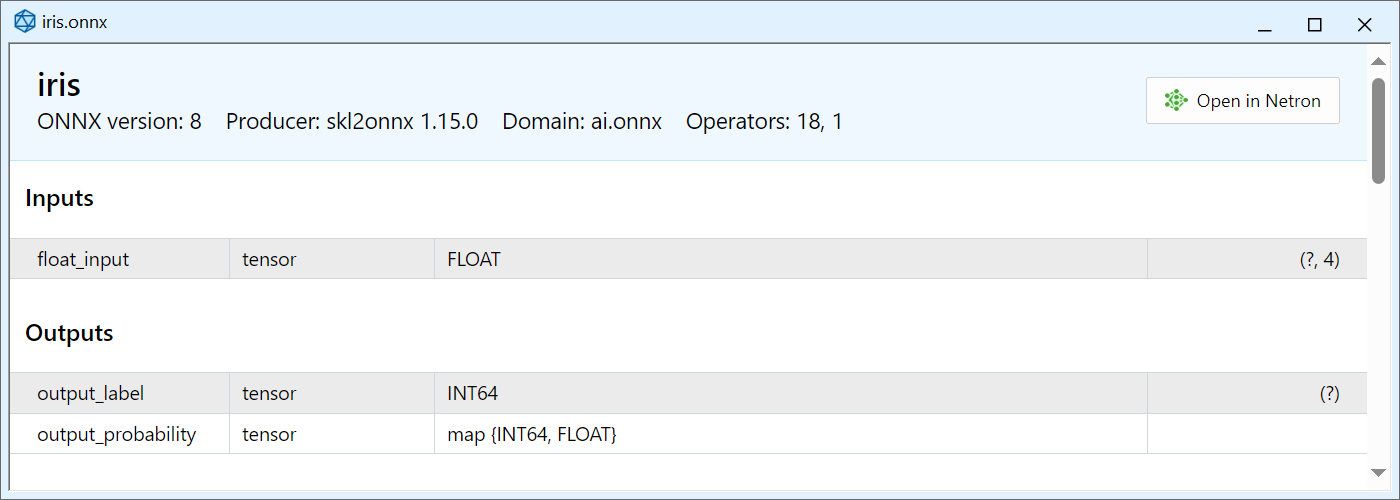
The Map sequence is passed as "output_probability". It has a key of INT64 type (which corresponds to long in MQL5) and the float type value. To receive data from this output, declare the following structure:
struct MyMap { long key[]; float value[]; };
Here we used dynamic arrays with appropriate types. In this case, we can use fixed arrays because the Map for this model always contains 3 key+value pairs.
Since the Map sequence is returned, an array of such structures should be passed as a parameter for receiving data from output_probability output. This array can be dynamic or fixed, in accordance with the properties of a particular model. Example:
//--- declare an array to receive data from the output layer output_probability MyMap output_probability[]; ... //--- model running OnnxRun(model,ONNX_DEBUG_LOGS,float_input,output_label,output_probability);
MetaEditor
- Fixed display of output types in the ONNX model viewer.
MetaTrader 5 Web Terminal build 3980
- Added Contact Broker section in the web terminal's main menu.
- Added error handling for SSL authentications. This authentication type is not supported in the web terminal. One-time passwords can be used instead.
- Fixed desktop platform download link in the main menu.
- Fixed
accounts managing dialog. If the broker does not provide the demo or
real account opening option, the relevant menu item will be hidden.
Terminal
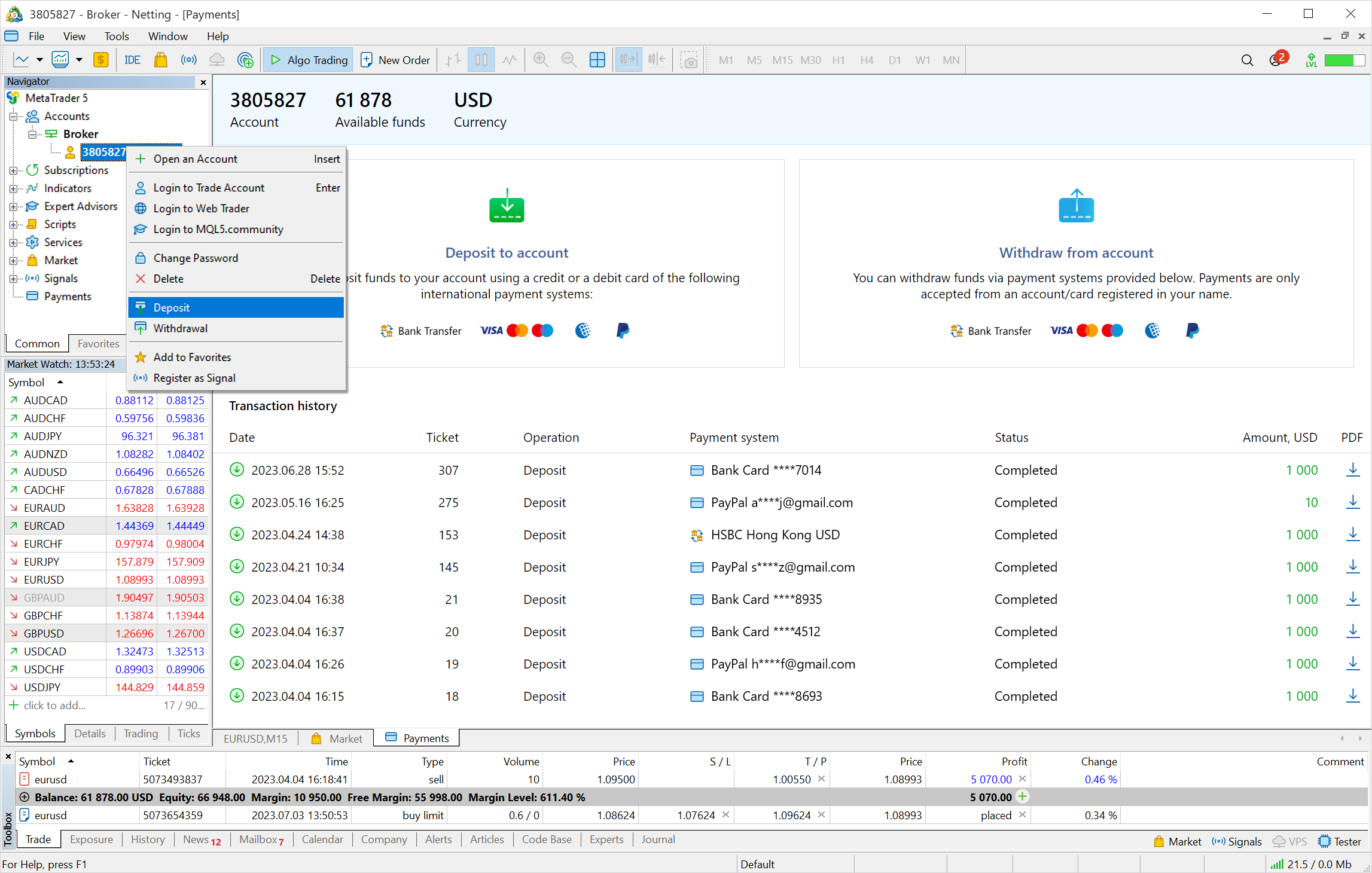
- Added support for balance operations for
depositing/withdrawing funds from a trading account directly in the
client terminal.
We have added integration of the most popular payment systems directly into the MetaTrader 5 platform, which allows brokers to provide traders with a new level of service. When depositing or topping up, simply select the method that suits you best and complete the transaction. For more convenience, traders can save selected cards so as not to enter card details each time. Brokers do not store payment details and card numbers. The payment data entered by a user is sent over a secure channel to the user-selected payment system.
The new functionality provides traders with the opportunity to manage funds in one click without leaving the client terminal.
-
Completely revamped the trading history report. Now it is more easy to
view. We have revised the approach to presenting information and
converted dry statistical reports into interactive graphs and diagrams.
The work is still in progress, but you can evaluate the changes already.
To view trading statistics, click Reports in the View menu.
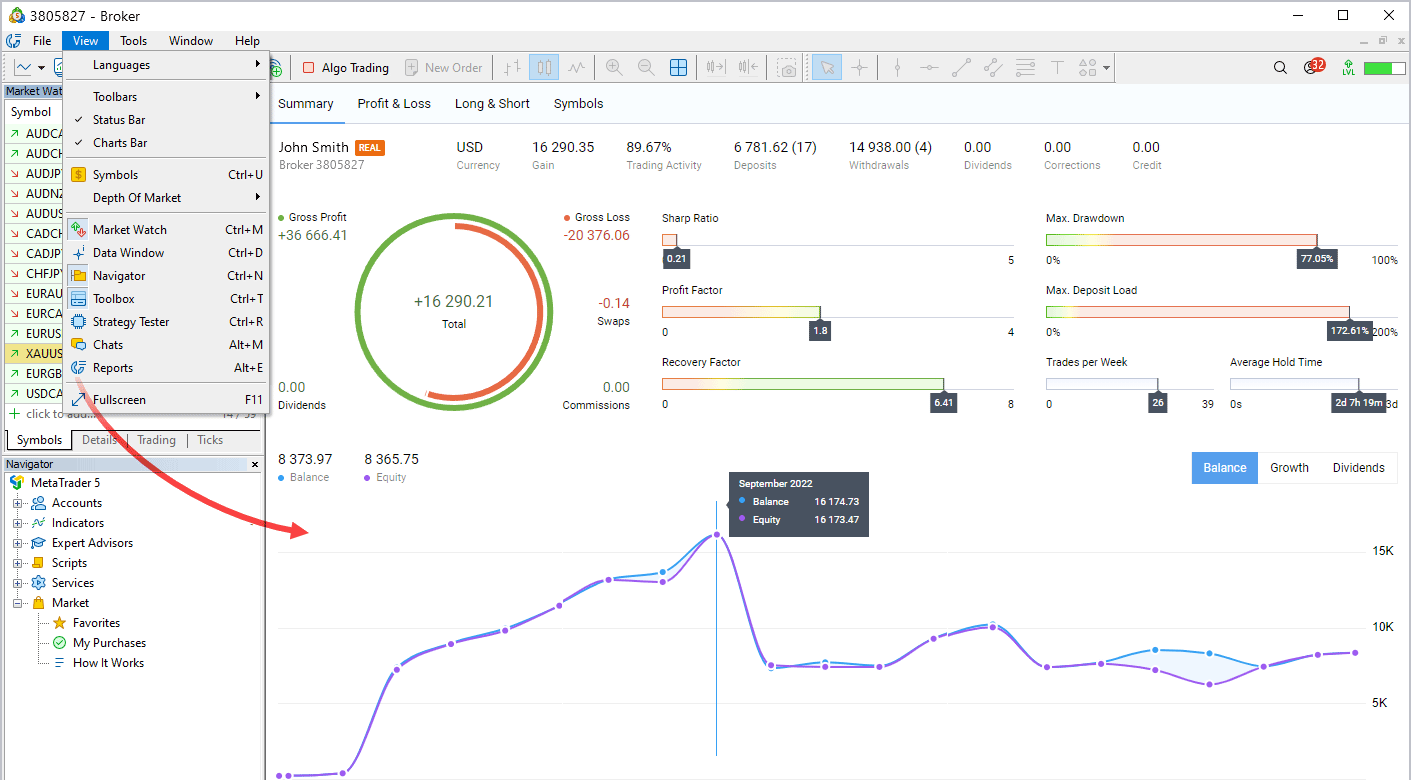
The report is divided into four tabs, each containing aggregated information:- Summary — trading summary: account data, overall profit and loss, deposits and withdrawals, balance, growth and dividends graphs and others.
- Profit/Lost — data on profitable and losing trades. The parameter is divided by types of trading (manual, algorithmic and copying trades). The results can be analyzed in terms of trades or money by months and years.
- Long/Short — dynamic ratio of purchases and sales at specified periods of time, as well as Buy and Sell profitability.
- Symbols — analysis of trades by financial instruments. Here you will see which symbols you earn or lose on, how often you trade them, graphs of trades and monetary volumes for them.
New reports allow you to visually evaluate trading results in a variety of aspects by simply clicking on the tabs. Histograms, graphs and diagrams are interactive and provide additional information when hovering the mouse cursor. Our designers have put much effort into making reports as simple and clear as possible. Just give them a try!
- Added the usage of AVX2 instructions
in case they are supported by CPU. This allows for more efficient use
of CPU capabilities the terminal is launched on. Now, when installing or
updating, the terminal determines the CPU architecture on its own and
installs the most optimal version. During the launch, the terminal sends
a message (AVX/AVX2) to the log displaying the set of instructions the
terminal is built for.
Terminal MetaTrader 5 x64 build 3914 started for MetaQuotes Software Corp. Terminal Windows 10 build 19045, 20 x Intel Xeon E5-2630 v4 @ 2.20GHz, AVX, 41 / 63 Gb memory, 58 / 280 Gb disk, UAC, GMT+2
Advanced Vector Extensions (AVX) is an extension of the x86 instruction set for Intel and AMD microprocessors proposed back in 2008. Further development has led to the appearance of AVX2 and AVX-512 (2013).
- In addition to the two versions of
MetaTrader 5 terminals on X64 and AVX, we have released the third
version of the desktop terminal compiled with direct support for AVX2
commands. At the same time, ONNX models now also work with support for
AVX2 commands.
- Added display of links to the
broker's necessary regulatory documents. You can now obtain all the
necessary legal information from your broker directly in the client
terminal in Help / Terms & Conditions.
- Fixed 2FA authorization in case of the additional use of the extended authorization using certificates.
- Fixed display of internal mail messages when working on MacOS.
- Fixed display of the Signals window when working in Wine.
- Released new MetaTrader 4 and 5 installers for Linux.
- Added commands for visiting Linux and Mac terminal version download pages
in Help. For traders' convenience, we have created a special section of
the website with terminal versions for all platforms, as well as for
trading in a browser.
- Fixed embedding images into internal mail.
- Released new MetaTrader 5 terminal installers for Mac with support for M1/M2 processors. Due to the transition to Wine 8.0.1, we strongly recommend that you remove old versions and install new ones. When using Wine versions older than 8.0.0, a message about the need for an update is displayed in the terminal log.
- Added "VPS Hosting
Speed Up" in the network scan menu indicating the ping to your trading
server. This allows you to clearly see how your network delays decrease
when renting a built-in VPS.
- Strengthened the requirements for minimum password complexity, namely:
- password length — at least 8 characters
- the password must contain at least 1 character in upper and lower case, at least 1 digit and at least 1 special character.
- Usable links in terminal logs. Now when double-clicking on lines with https links, users are sent to their browsers and the link is opened.
-
Fixed search for trading instruments in Market Watch. Now the symbol is
first searched by name, and then by other fields: description, ISIN,
etc.
- Fixed accounting for profit on trades when
calculating the balance in account trading history reports. In some
cases, the instrument type was not taken into account in the
calculations.
VPS Hosting
- Added the ability to send and run EX5 programs compiled under the x64/AVX/AVX2 command set. Programs for AVX512 are not supported on the built-in VPS.
- Increased the number of locations for renting the built-in VPS up to 27. Now the selection of the closest server has become even wider.
MQL5
-
Added control of compilation settings, including selection of extended
processor instruction sets — AVX, AVX2, AVX512 and FMA3.
Modern CPUs have a set of advanced instructions that significantly speed up mathematical calculations, but the vast majority of modern programs do not use these capabilities. We have added support for these instructions to the MQL5 language compiler, which allows for more efficient and faster code generation.
We have also added the ability to choose which type of instructions to compile an MQL5 program with. You can specify both general settings for single programs in MetaEditor Options, and apply personal ones in project settings: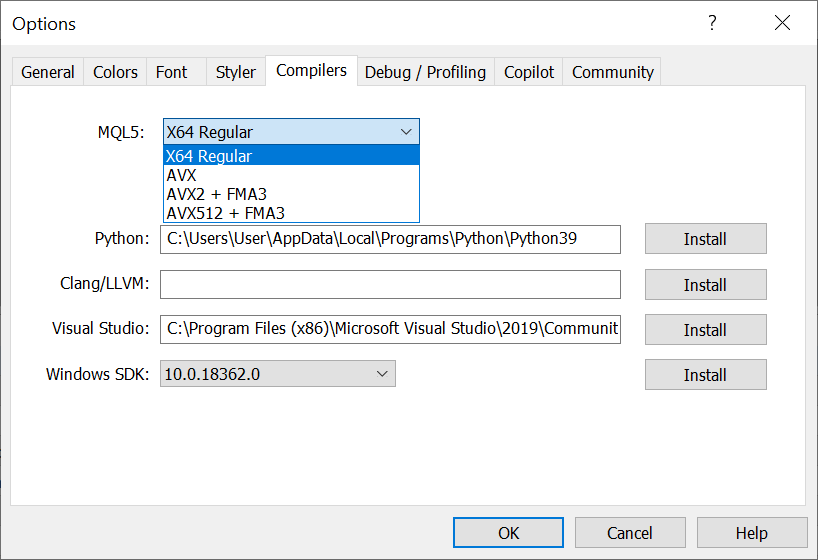
- Added the ENUM_AVERAGE_MODE and ENUM_CLASSIFICATION_METRIC enumerations to the Matrix and Vector Methods.
- Added Set method for vectors.
- Revised OpenCL initialization - now it is initialized by the first actual use, not by loading an MQL5 program containing OpenCL functions.
- Fixed an error when calling the SocketIsConnected function.
- Fixed delay in calling the OnDeinit method when unloading custom indicators.
- Fixed a compiler error, which caused incorrect calculation of the string length in the indicator_label property leading to incorrect display of tooltips for graphical objects.
- Fixed the use of multi-line comments in the macro body. An example of a macro where the error occurred:
#define MACRO1 /* #define MACRO2 */ void OnStart() { #ifdef MACRO2 Print( 2 ); #else Print( 1 ); #endif }
- Fixed the order of parameters of the MathAtan2 function. The order now matches the similar function in C++.
- Added the new TERMINAL_CPU_ARCHITECTURE value to the ENUM_TERMINAL_INFO_STRING
enumeration. Also, added the __CPU_ARCHITECTURE__ macro — obtaining
the CPU architecture of the computer the terminal is running on. Example
of use:
void OnStart() { Print("CPU name: ",TerminalInfoString(TERMINAL_CPU_NAME)); Print("CPU cores: ",TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_CPU_CORES)); Print("CPU architecture: ",TerminalInfoString(TERMINAL_CPU_ARCHITECTURE)); Print(""); Print("EX5 architecture: ",__CPU_ARCHITECTURE__); } CPU name: 12th Gen Intel Core i9-12900K CPU cores: 24 CPU architecture: AVX2 + FMA3 EX5 architecture: AVX
- Changed the extern modifier behavior. Now declaration of a variable with the extern modifier is a variable pre-declaration.
New restrictions: - The variable pre-declaration should not contain initialization. For
example, when compiling the code below, we get the error "X - extern
variable initialization is not allowed":
extern int X=0; void OnStart() { }
- The 'extern' variable should be declared in the
program without the 'extern' keyword. For example, when compiling the
code below, we get the error "unresolved extern variable X":
extern int X; void OnStart() { }
- When using 'extern', it is important to pay
attention to the initialization order, because a variable can be
accessed before it is initialized. For example, the following code will
yield "Y=0 X=5" in the log since initialization of variable Y occurs
before initialization of variable X:
extern int X; int Y=X; void OnStart(void) { Print("Y=",Y," X=",X); } int X=_Digits;
MetaEditor
- Added the usage of AVX2 instructions in case they are supported by CPU.
- Fixed an error occasionally causing freezes during compilation.
- Improved display of local variables when debugging.
Tester
- Added the usage of AVX2 instructions in case they are supported by CPU.
Updated user interface translations.
Fixed errors reported in crash logs.
MetaTrader 5 Web Terminal build 3950
- Added display of the Ask price to the chart settings.
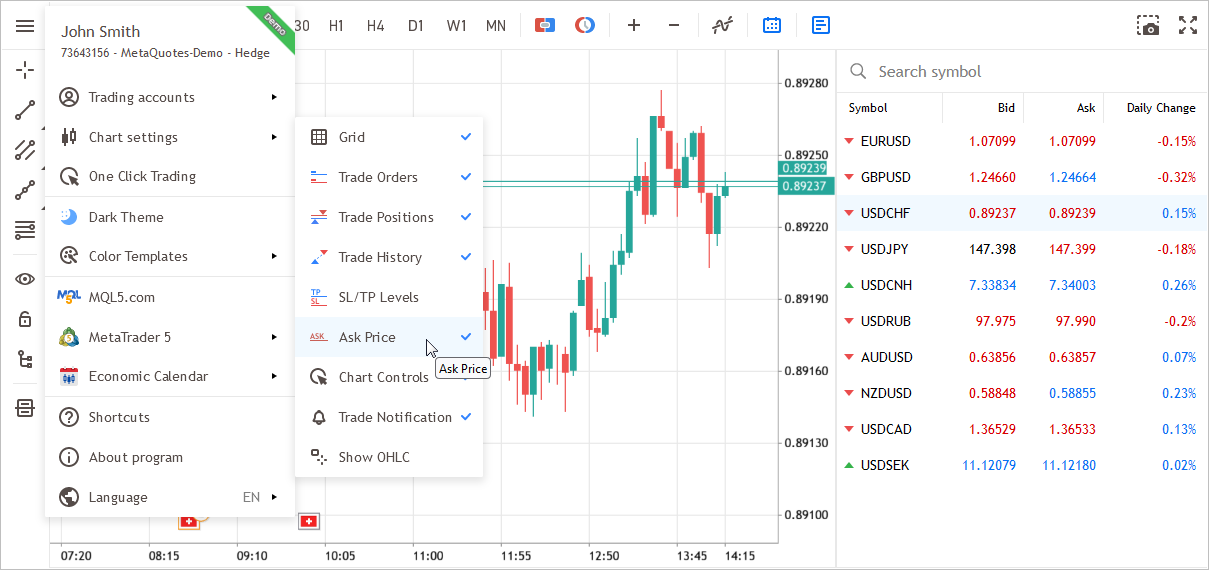
- Accelerated initial terminal loading.
- Added the ability to change the password.
- Added the ability to delete and save the password.
- Added a custom period for displaying trading history.
- Fixed forced password change.
- Fixed calculation of diff — the distance between the open price and TP/SL levels.
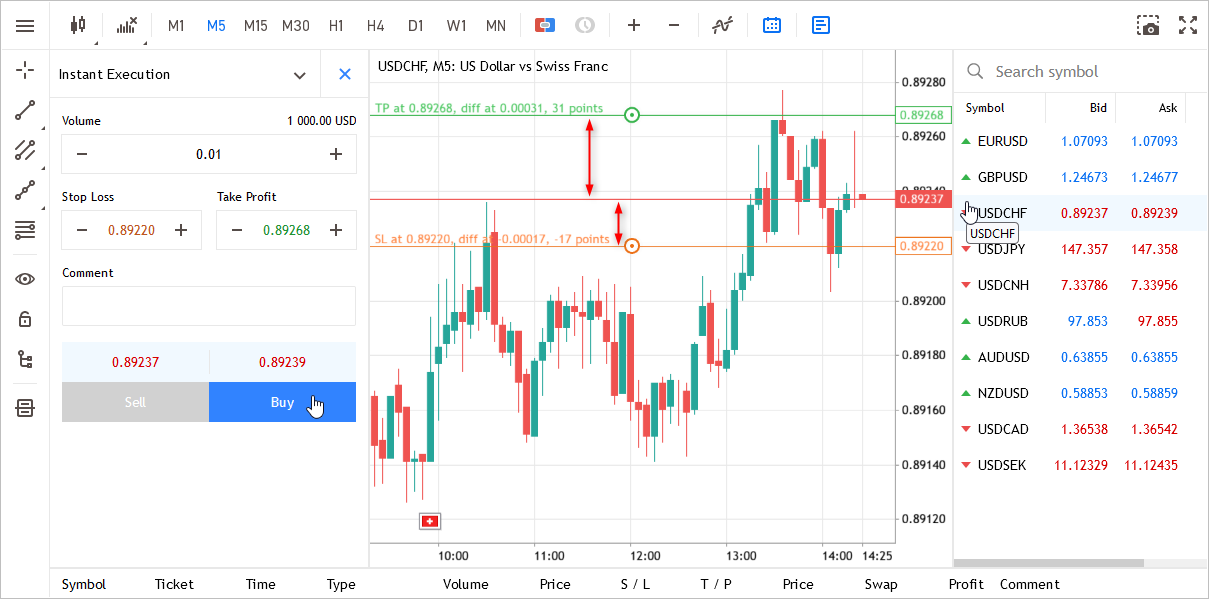
- Fixed ticks stop error when closing all orders/deals.
- Fixed display of Economic calendar events. Sometimes, they were not displayed on the chart despite the option being enabled.
- Fixed indicator reset when changing a chart symbol.
- Fixed an error in the form of opening a real account when confirming the phone/email.
- Added new translations and corrected existing ones.
Terminal
- Added support for the new order filling policy — Passive / Book or Cancel (BOC).
The BOC policy indicates that an order can only be placed in the Depth of Market (order book). If the order can be filled immediately when placed, this order is canceled. This policy guarantees that the price of the placed order will be worse than the current market price. BOC is used to implement passive trading: it is guaranteed that the order cannot be executed immediately when placed and thus it does not affect current liquidity. This filling policy is only supported for limit and stop limit orders in the Exchange Execution mode.
The availability of the new filling policy depends on the broker.
- The platform switches to using Microsoft Edge WebView2 for displaying the HTML content.
Compared to the outdated MSHTML, the new component significantly expands content displaying capabilities by providing access to modern technologies. The use of WebView2 improves the appearance of some platform sections, increases performance, and creates a more responsive interface. In particular, the new component will affect the Market, Signals and VPS sections.Full support for WebView2 was introduced in Windows 10. We strongly recommend that all users upgrade to the latest operating system version and install all available updates. The platform will continue to use MSHTML under Windows 7 and Wine, but the new features will not be available. The minimum recommended operating system version is Windows 10 21H2 (build 19044, November 2021).
- Improved Market
security system. Now, in order to run the product, the user must be
authorized in the platform with the same MQL5 account via which the
product was purchased. The account must be specified under the Tools \
Options \ Community section:
If no account or an invalid account is specified, the product will not start, and the following message will be printed in the platform journal:
'ProductName' requires active MQL5 account in Tools->Options->Community - Added Overview command to the history section context menu. The command opens a trading report for the account:
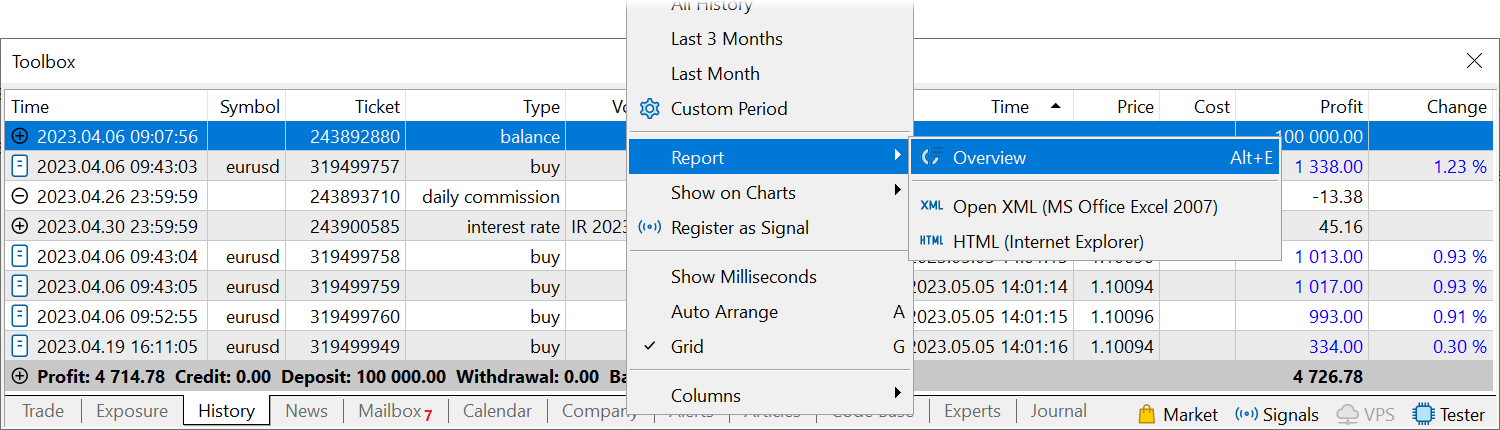
- Fixed display errors in the two-factor authentication dialog. If the terminal had several accounts with the same number but opened with different brokers, the account connection form could fail to display the one-time password field.
- Implemented faster rendering of indicators with the DRAW_COLOR_CANDLES display style.
- Fixed trading report creation errors. On-chart profit and equity values could be displayed incorrectly under certain conditions.
- Added display of Costs in the trading report. The value shows the total costs incurred when performing deals relative to the symbol's current mid-point price (mid-point spread cost). This is the amount which the trader lost due to the spread. The availability of this value depends on the broker.
- Updated UI translations.
- Improved stability under Wine, especially on macOS
systems. We recommend completely removing old terminals and
re-installing them:
- Accelerated package installation and updates downloading procedures. Improved analysis of AVX availability on the user's computer when selecting a distribution package.
- Enabled support for TLS 1.3 in web protocols. TLS 1.0 is considered deprecated and insecure and has therefore been disabled.
- Fixed accounting for agent commissions in trading history reports. The relevant transactions could be ignored when calculating the final profit.
- Fixed the inability to change the server in the account connection dialog. The issue arose when there were several accounts in the terminal with the same number from different brokers.
MQL5
- Added new STAT_COMPLEX_CRITERION value in the ENUM_STATISTICS enumeration. Use the property to obtain the calculated complex criterion value, as a result of optimization.
- Improved RegressionMetric
method used for calculating the regression metric based on the passed
matrix or vector. Added vector_true and matrix_true parameters for
passing true values which evaluate the predicted data quality.
double vector::RegressionMetric( const vector& vector_true, // true values const ENUM_REGRESSION_METRIC metric // metric ); double matrix::RegressionMetric( const matrix& matrix_true, // true values const ENUM_REGRESSION_METRIC metric // metric ); vector matrix::RegressionMetric( const matrix& matrix_true, // true values const ENUM_REGRESSION_METRIC metric, // metric const int axis // axis );
- Added the LinearRegression method. It returns a vector/matrix with calculated linear regression values for the passed vector/matrix.
vector vector::LinearRegression(); matrix matrix::LinearRegression( ENUM_MATRIX_AXIS axis=AXIS_NONE // axis along which regression is calculated );
Example:
vector vector_a; //--- fill the vector with prices vector_a.CopyRates(_Symbol,_Period,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,1,100); //--- get a linear regression vector vector_r=vector_a.LinearRegression();
The results are visualized in the graph:
- Added the HasNan method, which returns the number of NaN values in a matrix/vector.
ulong vector::HasNan(); ulong matrix::HasNan();
When comparing the appropriate pair of elements having NaN values, the Compare and CompareByDigits methods consider these elements equal, while in case of a usual comparison of floating-point numbers NaN != NaN.
-
Modified the OnnxTypeInfo structure which is used for operations with ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange) models:
struct OnnxTypeInfo { ENUM_ONNX_TYPE type; // parameter type OnnxTensorTypeInfo tensor; // tensor description OnnxMapTypeInfo map; // map description OnnxSequenceTypeInfo sequence; // sequence description };
The data type is specified in the structure using new substructures:
- OnnxTensorTypeInfo — tensor
- OnnxMapTypeInfo — map
- OnnxSequenceTypeInfo — sequence
struct OnnxTensorTypeInfo { ENUM_ONNX_DATATYPE data_type; // data type in the tensor long dimensions[]; // number of elements }; struct OnnxMapTypeInfo { ENUM_ONNX_DATA_TYPE key_type; // key type OnnxTypeInfo type_info; // value type }; struct OnnxSequenceTypeInfo { OnnxTypeInfo type_info; // data type in the sequence };
Depending on OnnxTypeInfo::type (ONNX_TYPE_TENSOR, ONNX_TYPE_MAP or ONNX_TYPE_SEQUENCE), the relevant substructure is filled.
- Improved support for ONNX models.
- Added CopyIndicatorBuffer methods which enable the obtaining of indicator buffer data into a vector.
bool vector<T>::CopyIndicatorBuffer(long indicator_handle,ulong buffer_index,ulong start_pos,ulong count); bool vector<T>::CopyIndicatorBuffer(long indicator_handle,ulong buffer_index,datetime start_time,ulong count); bool vector<T>::CopyIndicatorBuffer(long indicator_handle,ulong buffer_index,datetime start_time,datetime stop_time);
- Fixed operations with arrays having two or more dimensions in the FrameAdd and FrameNext methods.
- Fixed CRedBlackTree::Remove Standard Library method.
- Implemented fixes in the Fuzzy Logic library.
MetaEditor
- Added integration with the advanced automatic coding AI Assistant. Its operation is based on OpenAI models.
Enter a comment or part of a function and send a prompt. The neural
network will analyze the prompt and will offer coding options to
implement the idea.
Depending on the file type, the string "MQL5 language", "Python language" or "C++ language" is automatically inserted at each prompt beginning. Thus, the neural network will provide the result in the required language.
AI Assistant is currently free and is already enabled in the editor. There are several options available under Tools \ Options \ AI Assistant:
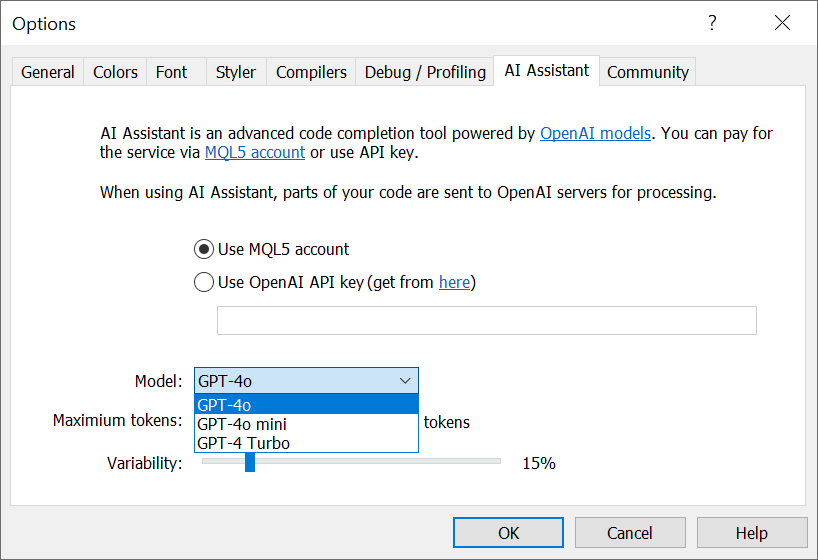
Payment settings:
- Use your MQL5 account: this option is currently available for free. Later, you will be able to pay for the subscription directly from your MQL5 account balance.
- Use an OpenAI key, if you have purchased a subscription and have the relevant key.
Prompt settings:
- Model — a neural network which will process your requests. text-davinci-003 and gpt-3.5-turbo are currently available. Support for gpt-4 will be added soon.
- Maximum tokens — the number of text units which the model can return in response to a prompt.
- Variability — affects how strictly the neural network will
follow the prompt. The bigger the value, the greater the result
randomness. This option corresponds to the temperature parameter in OpenAI models.
- Added ability to view the properties of ONNX models.
You can view the contents of the *.onnx file directly in the editor. As an example, find the project ONNX.Price.Prediction under Toolbox \ Public Projects and select Join in the context menu. The project will be downloaded to your computer and will appear in the Navigator.
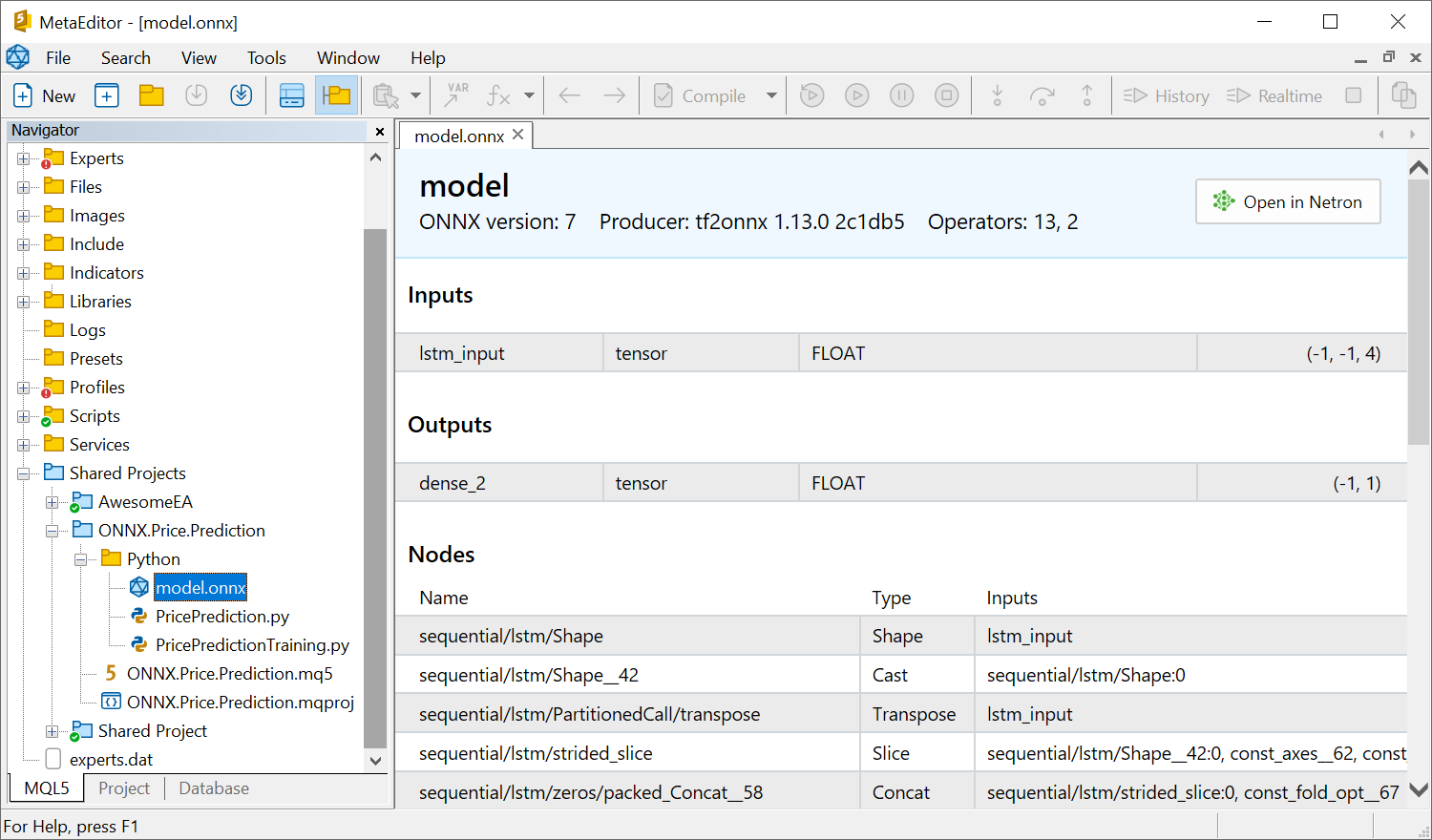
- Added ability to visualize machine learning models and neural networks using Netron. This viewer supports popular models, including ONNX, TensorFlow Lite, Caffe, Keras and ncnn, among others.
To view a model, select its file in the Navigator and click "Open in Netron". If this utility is not installed, its GitHub page will open, from which you can download the relevant installer, according to your operating system. For example, use Netron-Setup-X.X.X.exe for Windows. If the program is installed, the model will immediately open for viewing from the Navigator.
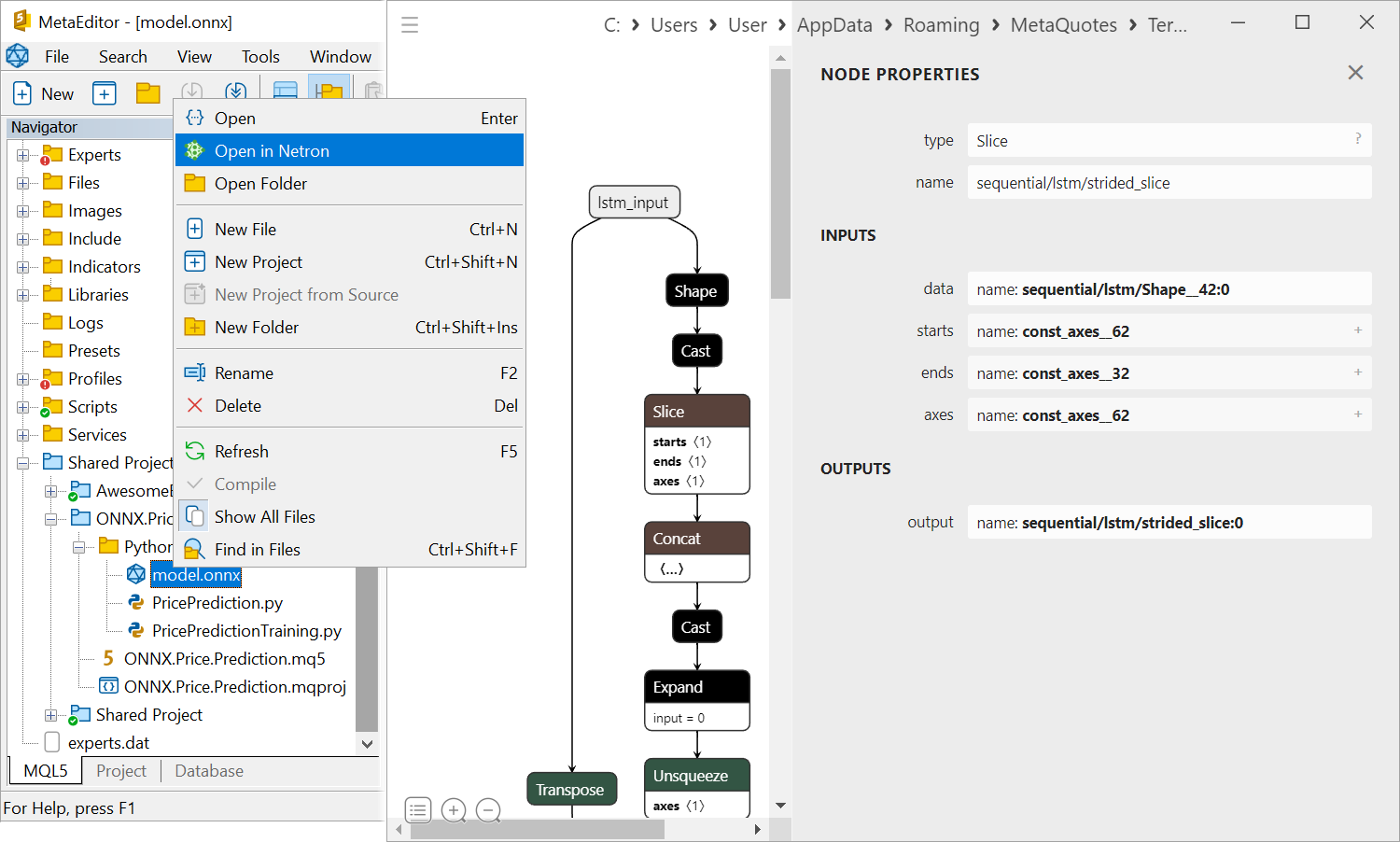
Supported formats:
- armnn, caffemodel, circle, ckpt, cmf, dlc, dnn, h5, har, hd5, hdf5, hn, keras, kmodel,
- lite, mar, meta, mge, mlmodel, mlnet, mlpackage, mnn, model, nb, ngf, nn, nnp,
- om, onnx, ort, paddle, param, pb, pbtxt, pdiparams, pdmodel, pdopt, pdparams, prototxt, pt, pth, ptl,
- rknn, t7, tfl, tflite, tmfile, tm, tnnproto, torchscript, uff, xmodel
- Updated UI translations.
Tester
- Fixed calculation of the "Average losing trade" metric in the testing report. Previously, the calculation could erroneously include entry deals if commissions were charged for such deals.
- Improved custom commission options in the strategy tester. To set a symbol, specify its name rather than the entire path.
- Updated icons in the strategy tester. New metaphors will make them easier to understand.
Fixed errors reported in crash logs.
Web Terminal
- Improved trading history section:
- Added display of balance operations in the trading history, such as deposits and withdrawals, commissions, and adjustments.
- Added display of totals in the trading history: balance, profit, commission, deposits, withdrawals and number of orders, among others.
- Added ability to sort operations and filter the history by depth in the mobile version.
- Enhanced symbol contract specifications. The following information has been added: volume limit, tick size and value, initial and hedged margin.
- Improved color schemes:
- Pending orders are displayed in gray on the chart. The
position color depends on the direction: red for Sell and blue for Buy.
The new colors provide easier navigation especially if a lot of
operations are displayed on the chart.
- When viewing/editing a position, only this position and its
levels are highlighted, while all other positions and orders become
gray, and their levels are hidden from the price scale. Thus, it will be
easier to manage separate operations.
- The Stop Loss color has been changed from red to orange to avoid confusion with Sell positions.
- Improved on-chart icons indicating position closing time. A
green icon is used for positions closed by Take Profit and a red one is
used for those closed by Stop Loss.
- Added interface translations into Arabic, Bulgarian, Vietnamese,
Greek, Indonesian, Malay, Dutch, Persian, Polish, Thai, Ukrainian and
Hindi. The web terminal is now available in 24 languages.
- Fixed Turkish UI translations.
- Fixed modification and deletion of pending orders in the Web Terminal mobile version.
- Fixed on-chart 'closed market' tooltip.
- Fixed display of profits in the position close button in the trading dialog. The error occurred during partial closing.
- Fixed display of on-chart trading notifications.
- Fixed volume modification using arrows in the Depth of Market.
- Fixed error which could cause the settings of running indicators to be reset under certain conditions.
- Fixed username checks when opening new accounts. Previously, an apostrophe in the name was considered an error.
- Fixed processing of requotes. The dialog with the requoted prices might not be displayed under certain conditions.
- Fixed display of the Ichimoku Kinko Hyo indicator. The
Chikou-Span, Up Kumo and Down Kumo lines will be displayed with the
correct offset.
- Fixed initial margin checks when opening new orders. The error occurred in the hedging position accounting system.
- Fixed scrolling in the contract specification window.
MQL5.community
- The MQL5 Cloud Network website has been completely redesigned: https://cloud.mql5.com.
Learn how to use the processing power of thousands of computers around the world to optimize your trading strategies. With the MQL5 Cloud Network, even the heaviest computations can be completed in a matter of minutes. Visit the website and find out how to participate in the network and how to earn money by providing your computer resources.
- Improved screenshot section in Market
products. Authors can upload images up to 1920*1800 pixels to
demonstrate how applications work. The screenshot gallery has also been
updated. The carousel shows image thumbnails, and a click on them opens
full-sized images.
- Freelance section improvements. Users will now receive more tips when placing their first orders:
- Requirements specification examples and a reminder to add one
- Order creation instructions
- Template usage tips
These tips can assist you in creating the order and in receiving the desired result.